A Geographic Portrait Of Japan: Unveiling The Archipelago Nation
By admin / April 19, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
A Geographic Portrait of Japan: Unveiling the Archipelago Nation
Related Articles: A Geographic Portrait of Japan: Unveiling the Archipelago Nation
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Geographic Portrait of Japan: Unveiling the Archipelago Nation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographic Portrait of Japan: Unveiling the Archipelago Nation
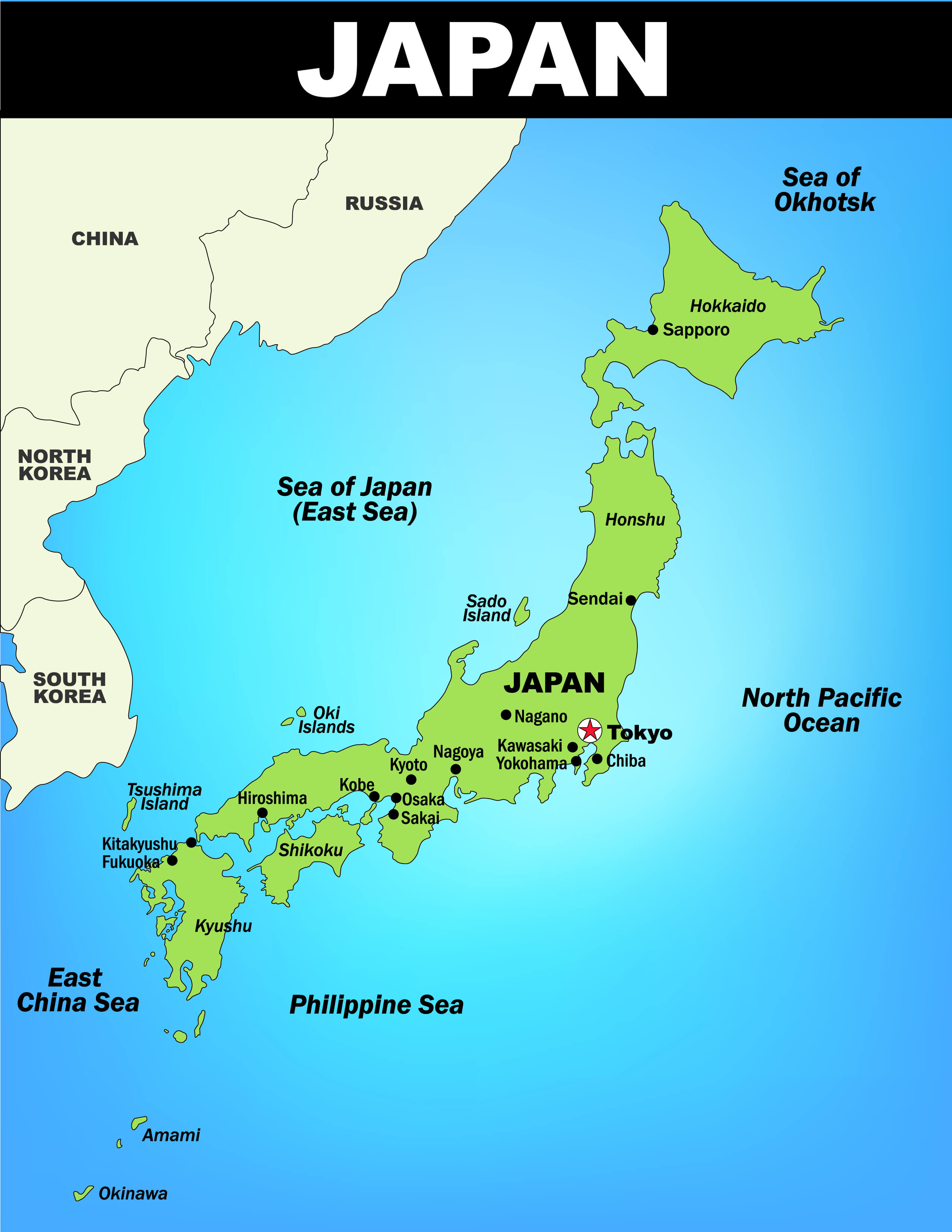
Japan, an island nation nestled in the northwest Pacific Ocean, is a captivating tapestry of diverse landscapes, vibrant culture, and a rich history. Its unique geography plays a crucial role in shaping its identity, influencing its natural environment, and driving its economic and societal development. Understanding the geographic map of Japan is essential for appreciating its complexities and appreciating the intricate relationship between its people and their environment.
Island Nation, Mountainous Terrain:
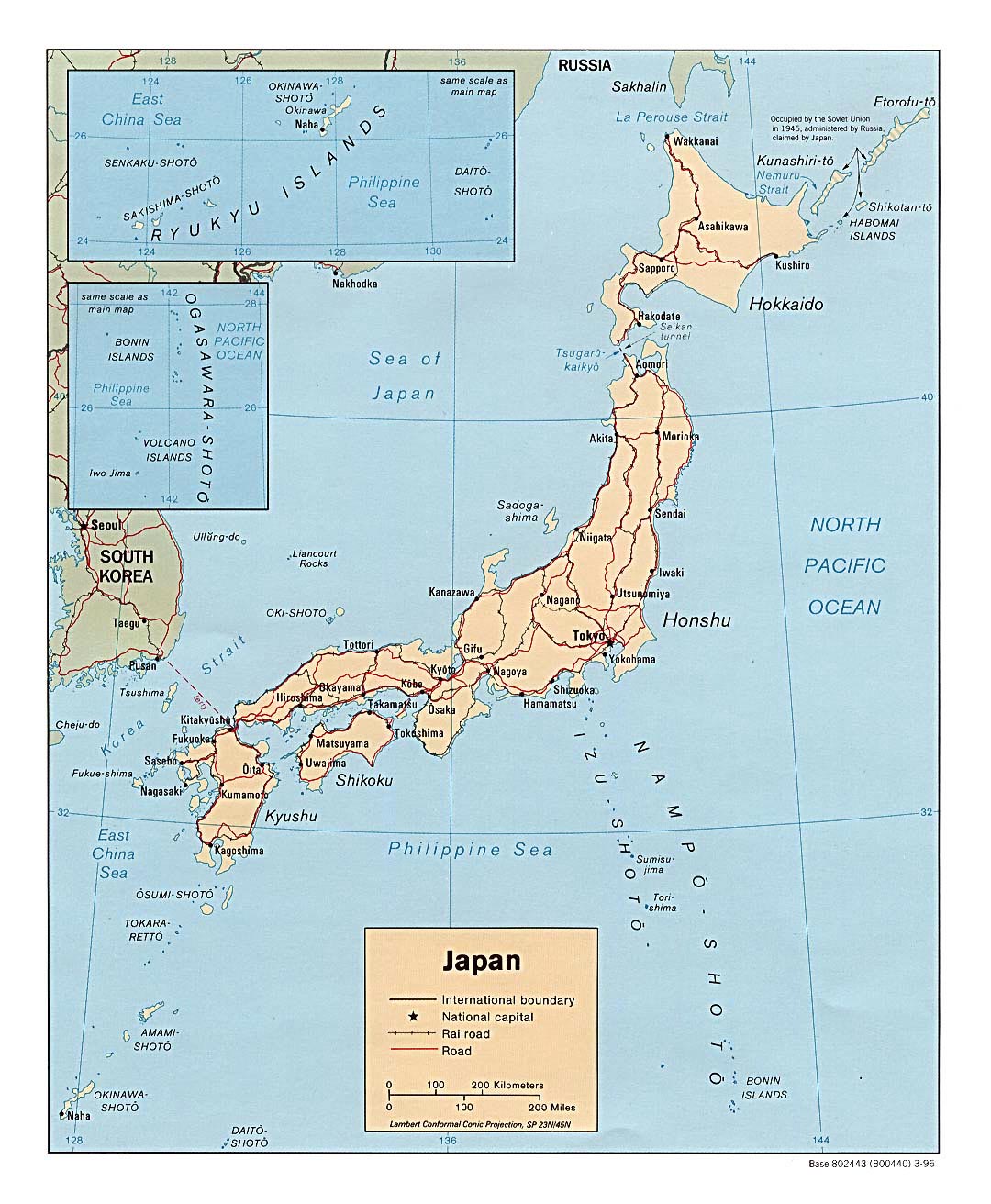
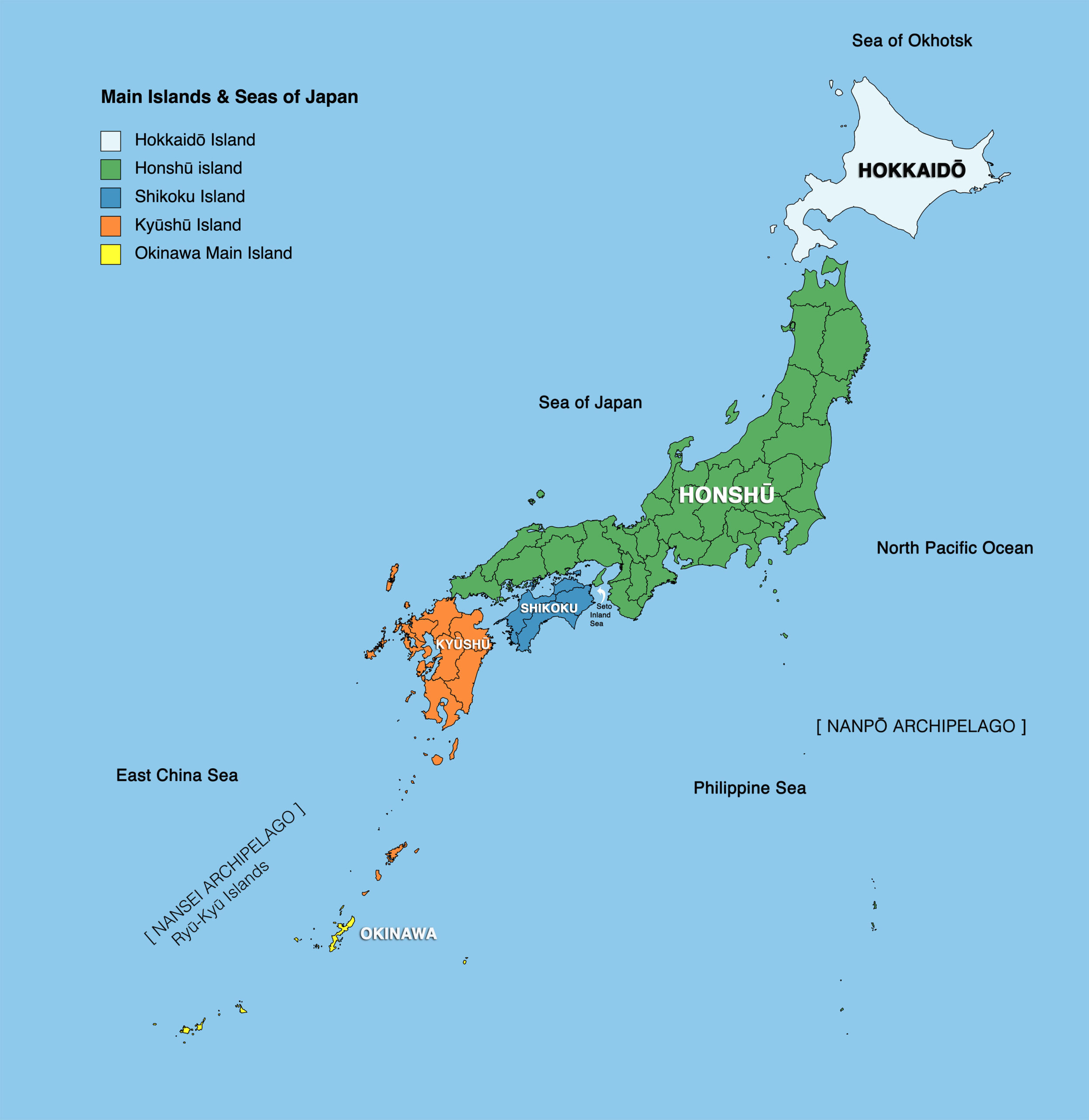
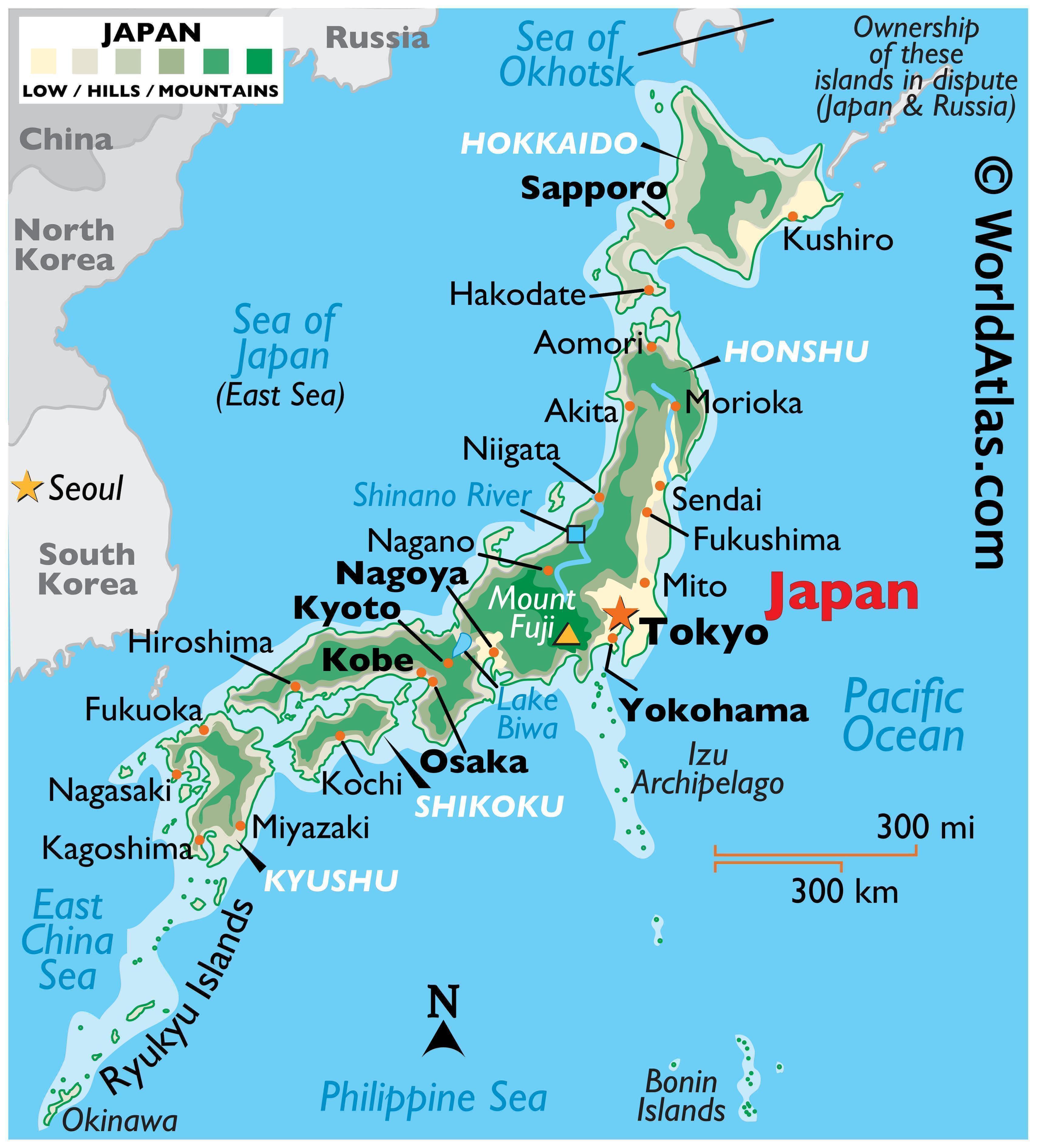
Japan’s geographic map reveals a nation composed of four main islands – Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu – and over 6,800 smaller islands. These islands are strung together like pearls on a necklace, creating a long, narrow coastline extending over 30,000 kilometers. The islands are predominantly mountainous, with approximately 73% of the land covered by forests and hills. The highest peak, Mount Fuji, stands as a majestic symbol of Japan, reaching a height of 3,776 meters.
Volcanic Activity and Tectonic Forces:
Japan’s position along the Pacific Ring of Fire, a zone of intense seismic activity, makes it prone to volcanic eruptions and earthquakes. This dynamic geological environment has shaped its landscape, creating volcanic mountains, hot springs, and fertile volcanic soils. The country experiences an average of 1,500 earthquakes annually, with some being significant. These events, while posing challenges, have also contributed to Japan’s unique cultural identity and resilience.
Climate and Vegetation:
Japan experiences a diverse range of climates due to its geographical location and topography. The northern island of Hokkaido has a cool, temperate climate with long winters, while the southern islands of Kyushu and Okinawa enjoy a subtropical climate with warm winters and humid summers. The country’s mountainous terrain also creates microclimates, with higher elevations experiencing colder temperatures and increased snowfall. This climatic variation supports a wide array of plant life, ranging from dense temperate forests in the north to subtropical vegetation in the south.
Rivers and Water Resources:
Japan is blessed with numerous rivers, with the longest being the Shinano River, flowing for over 367 kilometers. These rivers play a vital role in irrigation, transportation, and hydroelectric power generation. However, the country faces challenges in managing its water resources due to its mountainous terrain and seasonal variations in rainfall.
Urbanization and Population Distribution:
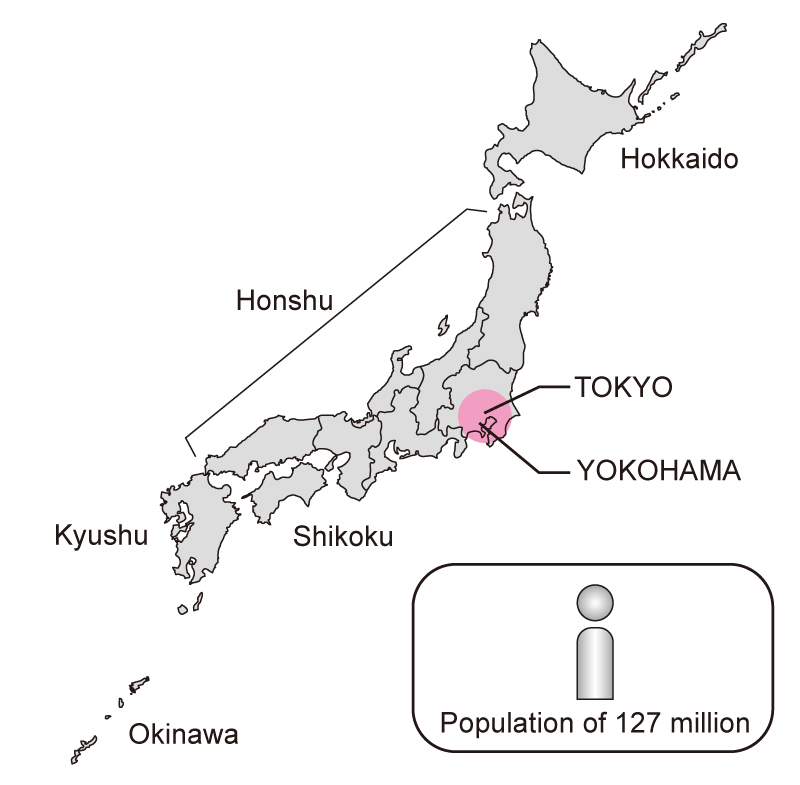
Despite its mountainous terrain, Japan has a high population density, concentrated primarily in its urban centers. The largest cities, Tokyo, Osaka, and Nagoya, form a densely populated "Golden Triangle" on the island of Honshu. This urbanization has led to the development of advanced infrastructure, economic hubs, and cultural centers. However, it has also raised concerns about environmental sustainability and the preservation of traditional rural landscapes.
Economic and Cultural Significance:
Japan’s geography has profoundly influenced its economic development and cultural identity. The country’s access to the Pacific Ocean has fostered a thriving fishing industry and maritime trade. Its mountainous terrain has promoted the development of traditional industries like forestry and agriculture. The country’s unique natural beauty has inspired its art, literature, and spirituality, fostering a deep connection between its people and their environment.
Geographic Map of Japan: A Tool for Understanding and Appreciation
The geographic map of Japan serves as a powerful tool for understanding the country’s complexities and appreciating its unique characteristics. It reveals the intricate relationship between its landforms, climate, and human activities. By studying the map, we gain insights into Japan’s history, culture, and its challenges and opportunities for the future.
FAQs on the Geographic Map of Japan:
1. What are the main islands of Japan?
The four main islands of Japan are Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu.
2. What is the highest peak in Japan?
The highest peak in Japan is Mount Fuji, standing at 3,776 meters.
3. What is the Pacific Ring of Fire, and how does it affect Japan?
The Pacific Ring of Fire is a zone of intense seismic activity encircling the Pacific Ocean. Japan’s location along this ring makes it prone to volcanic eruptions and earthquakes.
4. What are the main climate zones in Japan?
Japan experiences a diverse range of climates, from cool, temperate in the north to subtropical in the south.
5. What are the main rivers in Japan?
The longest river in Japan is the Shinano River, flowing for over 367 kilometers.
6. What are the major urban centers in Japan?
The largest cities in Japan include Tokyo, Osaka, and Nagoya.
7. How does Japan’s geography affect its economy?
Japan’s geography has influenced its economic development, fostering industries like fishing, forestry, and agriculture.
8. What are the environmental challenges facing Japan?
Japan faces challenges in managing its water resources, mitigating the impacts of natural disasters, and balancing urbanization with environmental sustainability.
Tips for Studying the Geographic Map of Japan:
- Focus on the key features: Pay attention to the four main islands, major mountain ranges, rivers, and major cities.
- Consider the scale: Understand the relative sizes of different features and the distances between them.
- Analyze the relationship between geography and human activities: How do the landforms, climate, and resources shape the lives of the Japanese people?
- Use online resources: Explore interactive maps, satellite imagery, and geographical databases to gain a deeper understanding.
- Compare Japan’s geography to other countries: How does Japan’s geography compare to its neighboring countries?
Conclusion:
The geographic map of Japan is a powerful tool for understanding the nation’s unique characteristics and appreciating its complex relationship with its environment. From its volcanic mountains to its diverse climates and bustling urban centers, Japan’s geography has shaped its history, culture, and economy. By studying the map, we gain insights into the challenges and opportunities facing this island nation, highlighting the intricate connection between its people and their environment.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographic Portrait of Japan: Unveiling the Archipelago Nation. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!