A Journey Through Mexico’s Waterways: Exploring The Country’s Rivers And Their Significance
By admin / July 5, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
A Journey Through Mexico’s Waterways: Exploring the Country’s Rivers and Their Significance
Related Articles: A Journey Through Mexico’s Waterways: Exploring the Country’s Rivers and Their Significance
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through Mexico’s Waterways: Exploring the Country’s Rivers and Their Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through Mexico’s Waterways: Exploring the Country’s Rivers and Their Significance

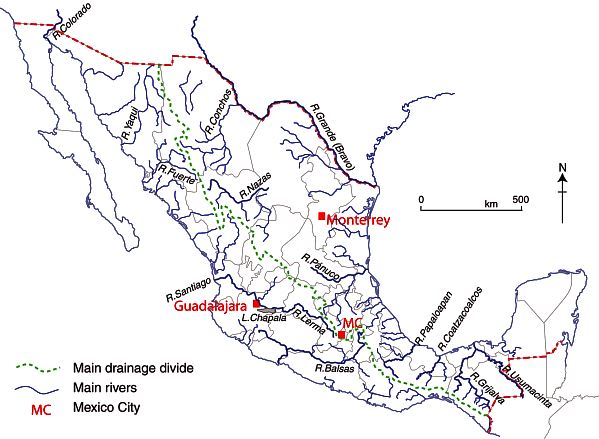
Mexico, a land of vibrant culture, diverse landscapes, and rich history, is also home to a vast network of rivers. These waterways, snaking their way across the country, play a crucial role in shaping the nation’s environment, economy, and cultural identity. Understanding the geography of Mexico’s rivers is essential to appreciating the complex tapestry of this fascinating nation.
The Major River Systems of Mexico
Mexico’s river systems can be broadly categorized into three main groups: those flowing into the Pacific Ocean, those flowing into the Gulf of Mexico, and those flowing into the interior basins.
Pacific Ocean Rivers:
- The Colorado River: The most prominent river in northwestern Mexico, the Colorado originates in the Rocky Mountains of the United States and flows through the Sonoran Desert before emptying into the Gulf of California. This river is a vital source of water for agriculture and drinking, and its dams provide hydroelectric power. However, the Colorado’s flow has been significantly reduced due to dam construction and water diversion, leading to ecological challenges in the delta.
- The Yaqui River: Located in the state of Sonora, the Yaqui River is a vital source of water for agriculture and the surrounding communities. Its flow is seasonal, with a significant decrease during the dry season. The Yaqui River has been the subject of controversy due to water rights disputes and the impact of mining activities on its flow.
- The Balsas River: The largest river flowing into the Pacific Ocean from Mexico, the Balsas River originates in the Sierra Madre Occidental and flows through the states of Guerrero and Michoacán before emptying into the Pacific Ocean. The Balsas River is known for its steep gradient and its role in the development of hydroelectric power.
Gulf of Mexico Rivers:
- The Río Bravo (Rio Grande): The Rio Grande, a major international river, forms the boundary between Mexico and the United States. It originates in the Rocky Mountains and flows southward through Texas and Mexico before emptying into the Gulf of Mexico. The Rio Grande plays a vital role in agriculture, drinking water supply, and the ecosystem of the border region. However, its flow has been significantly reduced due to dam construction and water diversion, leading to ecological challenges in the lower reaches.
- The Pánuco River: The Pánuco River, the largest river flowing into the Gulf of Mexico from Mexico, originates in the Sierra Madre Oriental and flows through the states of San Luis Potosí, Hidalgo, and Veracruz before emptying into the Gulf of Mexico. The Pánuco River is a vital source of water for agriculture and industrial activities, and its delta is a crucial habitat for a variety of wildlife.
- The Grijalva River: The Grijalva River, the longest river flowing into the Gulf of Mexico from Mexico, originates in the Sierra Madre de Chiapas and flows through the states of Chiapas and Tabasco before emptying into the Gulf of Mexico. The Grijalva River is a vital source of water for agriculture and hydroelectric power.
Interior Basin Rivers:
- The Lerma River: The Lerma River, the longest river flowing into an interior basin in Mexico, originates in the Nevado de Toluca volcano and flows through the states of México, Querétaro, and Guanajuato before emptying into Lake Chapala. The Lerma River is a vital source of water for agriculture and drinking, and its basin is home to a diverse range of ecosystems.
- The Nazas River: The Nazas River, located in the state of Durango, is a seasonal river that flows through the Chihuahuan Desert before emptying into the Bolson de Mapimí, a closed basin. The Nazas River is a vital source of water for agriculture, but its flow has been significantly reduced due to dam construction and water diversion, leading to ecological challenges in the basin.
The Significance of Mexico’s Rivers
Mexico’s rivers are not merely geographical features; they are integral to the country’s well-being. Their significance can be seen in the following ways:
- Water Supply: Rivers are the primary source of freshwater for millions of Mexicans, providing water for drinking, irrigation, and industrial use. The availability of water resources directly impacts the country’s agricultural production, economic development, and overall quality of life.
- Hydroelectric Power: Many rivers in Mexico have been harnessed for hydroelectric power generation, providing a significant portion of the country’s electricity supply. Hydroelectric dams play a crucial role in meeting the growing energy demands of Mexico’s population.
- Transportation: Rivers have historically played a vital role in transportation, connecting communities and facilitating trade. While the importance of river transportation has declined with the development of road and rail networks, some rivers remain important for the movement of goods and people in certain regions.
- Ecosystems and Biodiversity: Rivers and their surrounding ecosystems are home to a rich diversity of flora and fauna. These ecosystems provide crucial habitats for a wide range of species, including fish, birds, mammals, and reptiles. The health of these ecosystems is essential for maintaining biodiversity and ecological balance.
- Cultural Significance: Rivers have played a significant role in shaping the cultural identity of Mexico. Many indigenous communities have lived along rivers for centuries, relying on them for sustenance, transportation, and spiritual connection. Rivers are often depicted in art, literature, and music, reflecting their deep cultural significance.
Challenges Facing Mexico’s Rivers
Despite their importance, Mexico’s rivers face a number of challenges, including:
- Water Scarcity: Growing populations and increasing water demands from agriculture and industry have led to water scarcity in many regions. This has resulted in competition for water resources, conflicts between different user groups, and environmental degradation.
- Pollution: Industrial and agricultural activities, as well as sewage discharge, have resulted in pollution of many rivers, impacting water quality and threatening human health and aquatic ecosystems.
- Dam Construction: While dams provide benefits in terms of hydroelectric power and water storage, they can also have negative impacts on river ecosystems, disrupting natural flows and affecting fish populations.
- Climate Change: Climate change is expected to exacerbate existing challenges, with changes in precipitation patterns and increased temperatures leading to more frequent droughts and floods, further stressing water resources.
Addressing the Challenges
Addressing the challenges facing Mexico’s rivers requires a multifaceted approach involving:
- Sustainable Water Management: Implementing water conservation measures, promoting efficient irrigation techniques, and developing alternative water sources are crucial steps towards ensuring sustainable water management.
- Pollution Control: Stricter regulations and enforcement measures are needed to reduce industrial and agricultural pollution and improve sewage treatment infrastructure.
- River Restoration: Restoring degraded river ecosystems through habitat restoration, removal of dams, and reintroduction of native species can help improve water quality and biodiversity.
- Climate Change Adaptation: Developing strategies to adapt to the impacts of climate change, such as drought-resistant crops and improved flood management systems, is essential for ensuring the long-term sustainability of water resources.
FAQs on Mexico’s Rivers
Q: What is the longest river in Mexico?
A: The longest river in Mexico is the Río Bravo (Rio Grande), which forms the border between Mexico and the United States.
Q: What is the largest river in Mexico?
A: The largest river in Mexico, in terms of discharge, is the Grijalva River, which flows into the Gulf of Mexico.
Q: What is the most important river in Mexico?
A: The importance of a river depends on its specific context. However, the Rio Grande is considered particularly important due to its role as an international boundary, its significance for agriculture and drinking water supply, and its impact on the ecosystems of the border region.
Q: What are the main uses of Mexico’s rivers?
A: Mexico’s rivers are primarily used for water supply, hydroelectric power generation, transportation, and ecosystem support.
Q: What are the main threats to Mexico’s rivers?
A: The main threats to Mexico’s rivers include water scarcity, pollution, dam construction, and climate change.
Tips for Exploring Mexico’s Rivers
- Visit a river delta: The deltas of Mexico’s rivers are often rich in biodiversity and offer unique opportunities for wildlife viewing.
- Go rafting or kayaking: Many rivers in Mexico are suitable for rafting or kayaking, providing an adventurous way to experience the natural beauty of the country.
- Learn about local communities: Many communities in Mexico have a deep connection to their local rivers. Visiting these communities can provide insights into the cultural significance of rivers and the challenges they face.
- Support sustainable tourism: Choose tour operators who promote responsible tourism practices and support conservation efforts.
Conclusion
Mexico’s rivers are vital arteries, nourishing the nation’s environment, economy, and culture. Understanding the complexities of these waterways is crucial for appreciating the rich tapestry of this fascinating country. As Mexico faces the challenges of water scarcity, pollution, and climate change, it is essential to prioritize sustainable management of its rivers to ensure their long-term health and the well-being of the people who depend on them.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through Mexico’s Waterways: Exploring the Country’s Rivers and Their Significance. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!