A Strategic Landscape: Understanding The Deployment Of US Army Bases
By admin / April 22, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
A Strategic Landscape: Understanding the Deployment of US Army Bases
Related Articles: A Strategic Landscape: Understanding the Deployment of US Army Bases
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Strategic Landscape: Understanding the Deployment of US Army Bases. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Strategic Landscape: Understanding the Deployment of US Army Bases

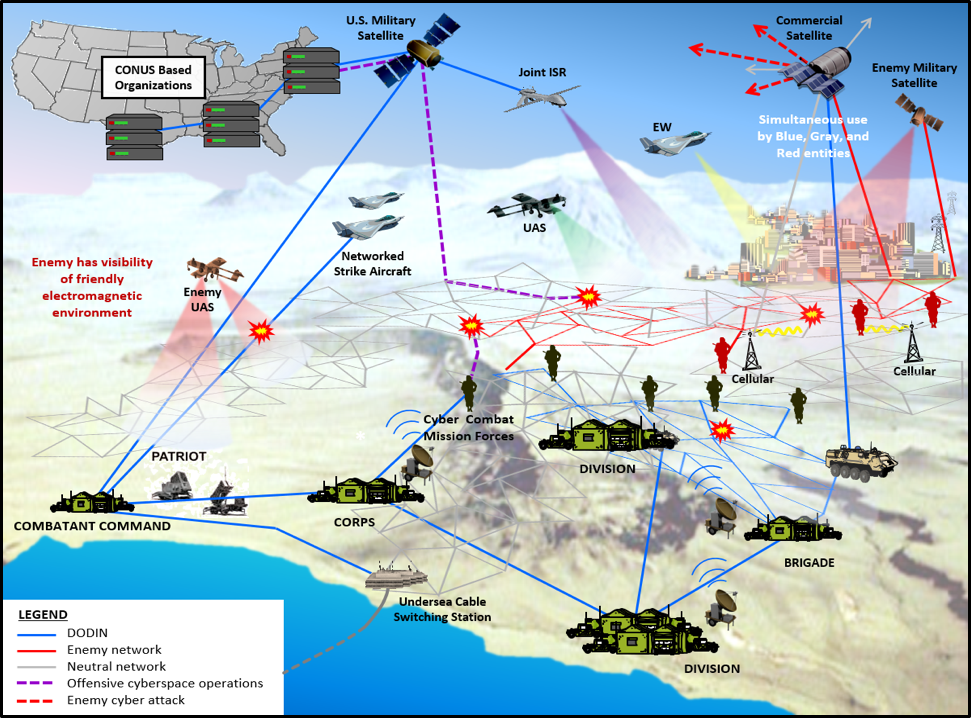
The United States Army, a cornerstone of national defense, maintains a vast network of bases across the globe. These installations, strategically positioned to respond to a range of potential threats, serve as hubs for training, logistics, and deployment. A comprehensive understanding of the US Army’s base structure offers valuable insights into the nation’s defense strategy, its global commitments, and the intricate network that supports its military operations.
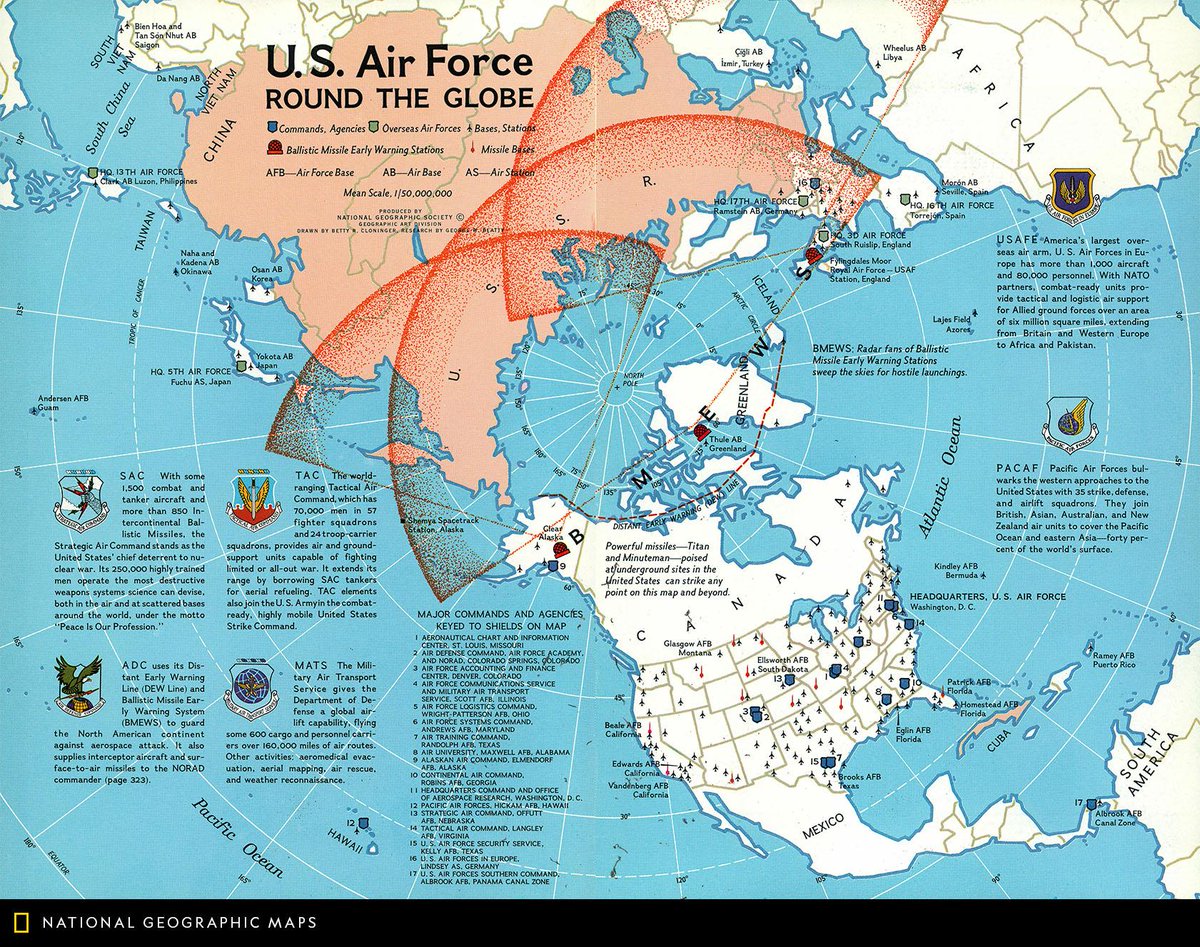
The Global Footprint:
The US Army’s global footprint encompasses a diverse array of installations, each serving a unique purpose. These bases are broadly categorized as:
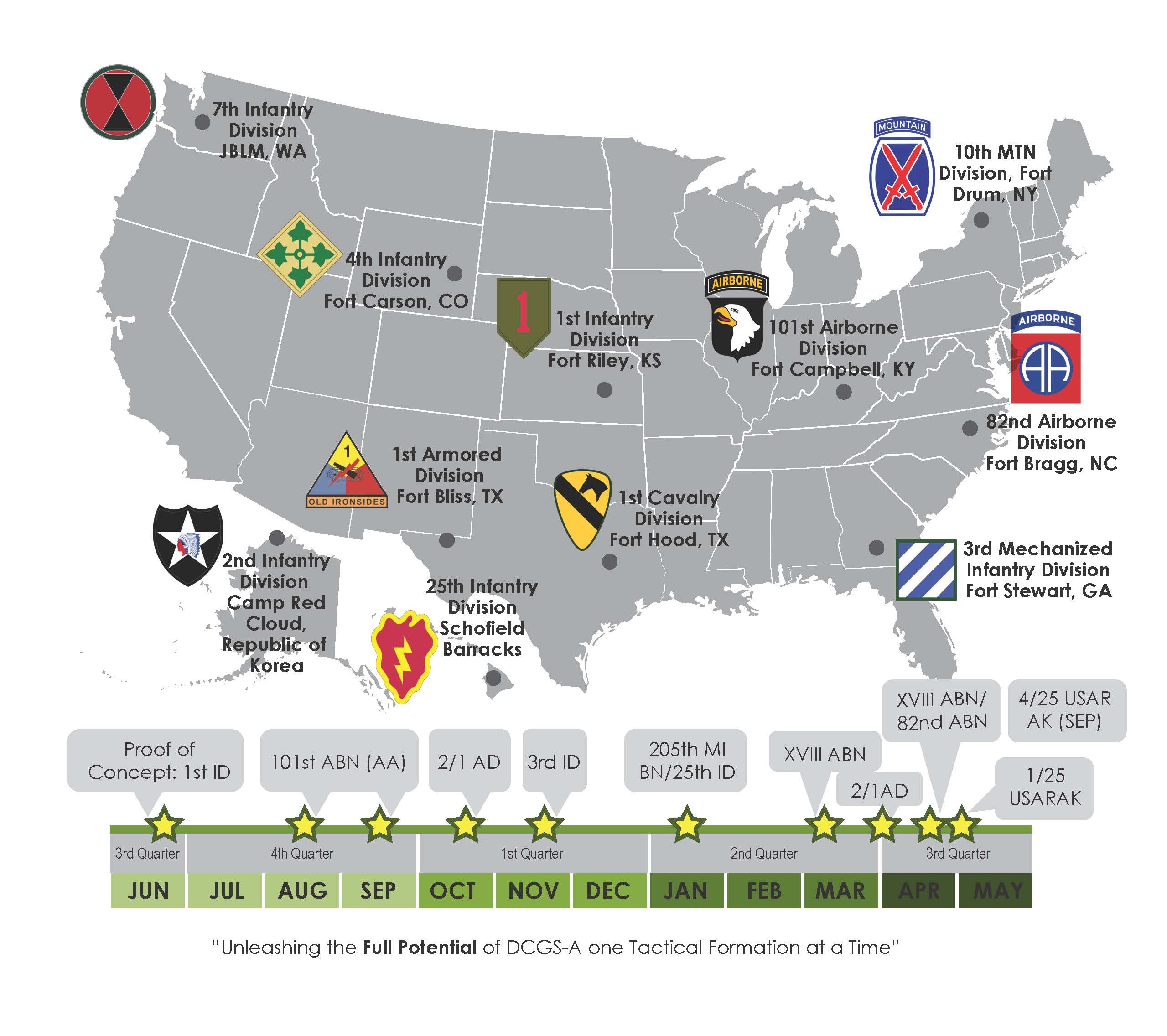
- Continental United States (CONUS) Bases: These installations, located within the United States, serve as training centers, logistical hubs, and command centers. Notable examples include Fort Bragg in North Carolina, Fort Hood in Texas, and Fort Carson in Colorado.
- Overseas Bases: These installations, strategically positioned across the globe, provide a forward presence, enabling rapid deployment and support for regional security operations. Notable examples include Camp Humphreys in South Korea, Camp Arifjan in Kuwait, and Ramstein Air Base in Germany.
Strategic Considerations:
The location and function of US Army bases are carefully considered, reflecting a complex interplay of geopolitical factors, regional security dynamics, and strategic objectives. These considerations include:
- Regional Security: The US Army maintains a presence in regions considered strategically vital, such as the Middle East, East Asia, and Europe. These bases serve as deterrents to potential adversaries and provide logistical support for ongoing operations.
- Alliance Partnerships: The US Army’s global network of bases strengthens its alliances with key partners, fostering cooperation and interoperability. These partnerships enhance collective security and enable joint operations.
- Force Projection: Overseas bases facilitate rapid deployment of forces, enabling the US Army to respond swiftly to crises and contingencies. This capability ensures a robust response to potential threats and supports global stability.
- Training and Exercises: US Army bases host a wide range of training exercises, enhancing combat readiness and fostering interoperability with allied forces. These exercises contribute to the development of tactical skills and the refinement of operational plans.
Navigating the Map:
The US Army’s base structure is a complex and dynamic entity, constantly evolving in response to shifting global dynamics. Understanding the map of US Army bases requires a comprehensive approach, considering factors such as:
- Base Size and Capacity: The size and capacity of US Army bases vary significantly, reflecting their specific missions and operational requirements.
- Infrastructure and Resources: Bases are equipped with diverse infrastructure and resources, including training facilities, barracks, hospitals, and logistical support systems.
- Personnel and Equipment: The number of personnel and equipment stationed at each base varies based on its mission and strategic importance.
Importance and Benefits:
The US Army’s global network of bases plays a crucial role in maintaining global security and stability. These installations provide:
- Deterrence: A visible military presence deters potential adversaries and discourages aggression.
- Response Capability: Strategic positioning enables rapid deployment of forces, allowing for a swift response to crises.
- Regional Stability: US Army bases contribute to regional stability by fostering cooperation and deterring conflict.
- Training and Interoperability: Bases provide essential training facilities and opportunities for joint exercises with allies, enhancing combat readiness and interoperability.
- Logistical Support: Bases serve as logistical hubs, ensuring the timely delivery of supplies and equipment to deployed forces.
FAQs:
Q: What are the largest US Army bases in the world?
A: The largest US Army bases in the world are:
- Fort Bragg, North Carolina (US): Home to the XVIII Airborne Corps and the Special Forces Command, Fort Bragg is a sprawling installation known for its extensive training facilities.
- Fort Hood, Texas (US): Housing the I Corps and the III Corps, Fort Hood is a major training center and deployment hub.
- Camp Humphreys, South Korea: The largest US Army base in South Korea, Camp Humphreys serves as a vital logistical hub and a key element of the US-South Korea alliance.
Q: How does the US Army maintain security at its overseas bases?
A: The US Army employs a multi-layered approach to base security, including:
- Physical Security: Perimeter fencing, guard posts, and surveillance systems are deployed to deter unauthorized access.
- Force Protection: Armed guards and military police are stationed at bases to maintain order and respond to threats.
- Intelligence Gathering: Intelligence agencies monitor potential threats and provide early warning of potential security risks.
- Cooperation with Host Nations: The US Army collaborates with host nations to enhance base security and ensure the safety of personnel.
Tips:
- Explore Online Resources: Numerous websites provide detailed information on US Army bases, including their locations, missions, and historical significance.
- Visit Military Museums: Military museums offer insights into the history and development of US Army bases.
- Engage with Veterans: Veterans can provide firsthand accounts of life on US Army bases and the challenges they faced.
Conclusion:
The US Army’s global network of bases is a testament to the nation’s commitment to national defense and international security. These installations, strategically positioned across the globe, serve as vital hubs for training, logistics, and deployment. Understanding the map of US Army bases offers valuable insights into the nation’s defense strategy, its global commitments, and the intricate network that supports its military operations. As the global security landscape continues to evolve, the US Army’s base structure will undoubtedly adapt to meet emerging challenges and ensure the nation’s continued security.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Strategic Landscape: Understanding the Deployment of US Army Bases. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!