A Topographical Journey Through Asia: Unveiling The Land’s Diverse Landscape
By admin / April 6, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
A Topographical Journey Through Asia: Unveiling the Land’s Diverse Landscape
Related Articles: A Topographical Journey Through Asia: Unveiling the Land’s Diverse Landscape
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Topographical Journey Through Asia: Unveiling the Land’s Diverse Landscape. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Topographical Journey Through Asia: Unveiling the Land’s Diverse Landscape

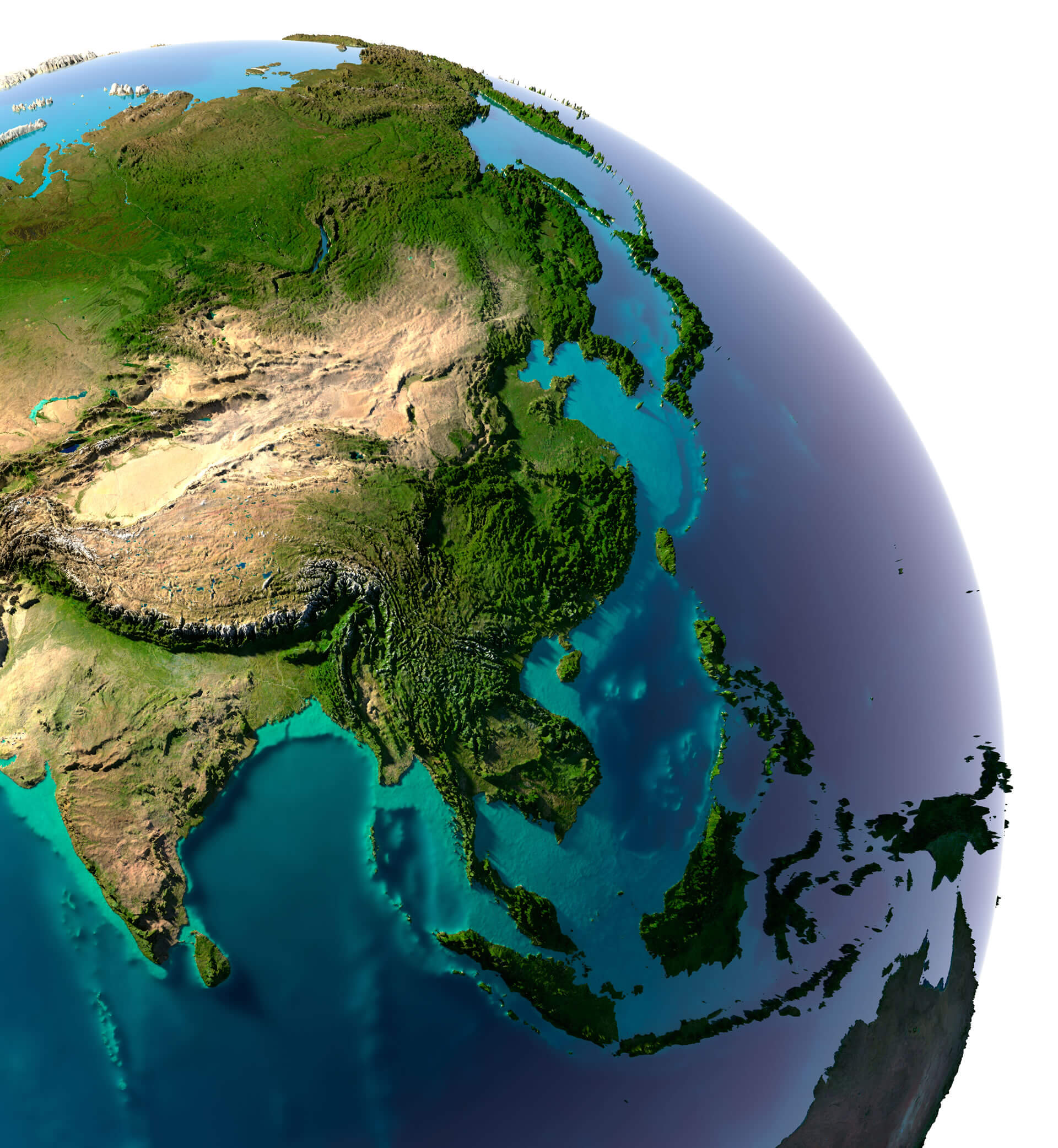
Asia, the largest and most populous continent, is a tapestry of diverse landscapes, from towering mountain ranges to vast plains, from fertile river deltas to arid deserts. Understanding the intricate interplay of these topographical features is crucial for comprehending the continent’s unique geographical character, its ecological systems, and the human civilizations that have flourished within its boundaries. Topographical maps, with their intricate lines and symbols, provide a visual key to unlocking these complexities.
The Lay of the Land: Delving into Asia’s Topographical Features
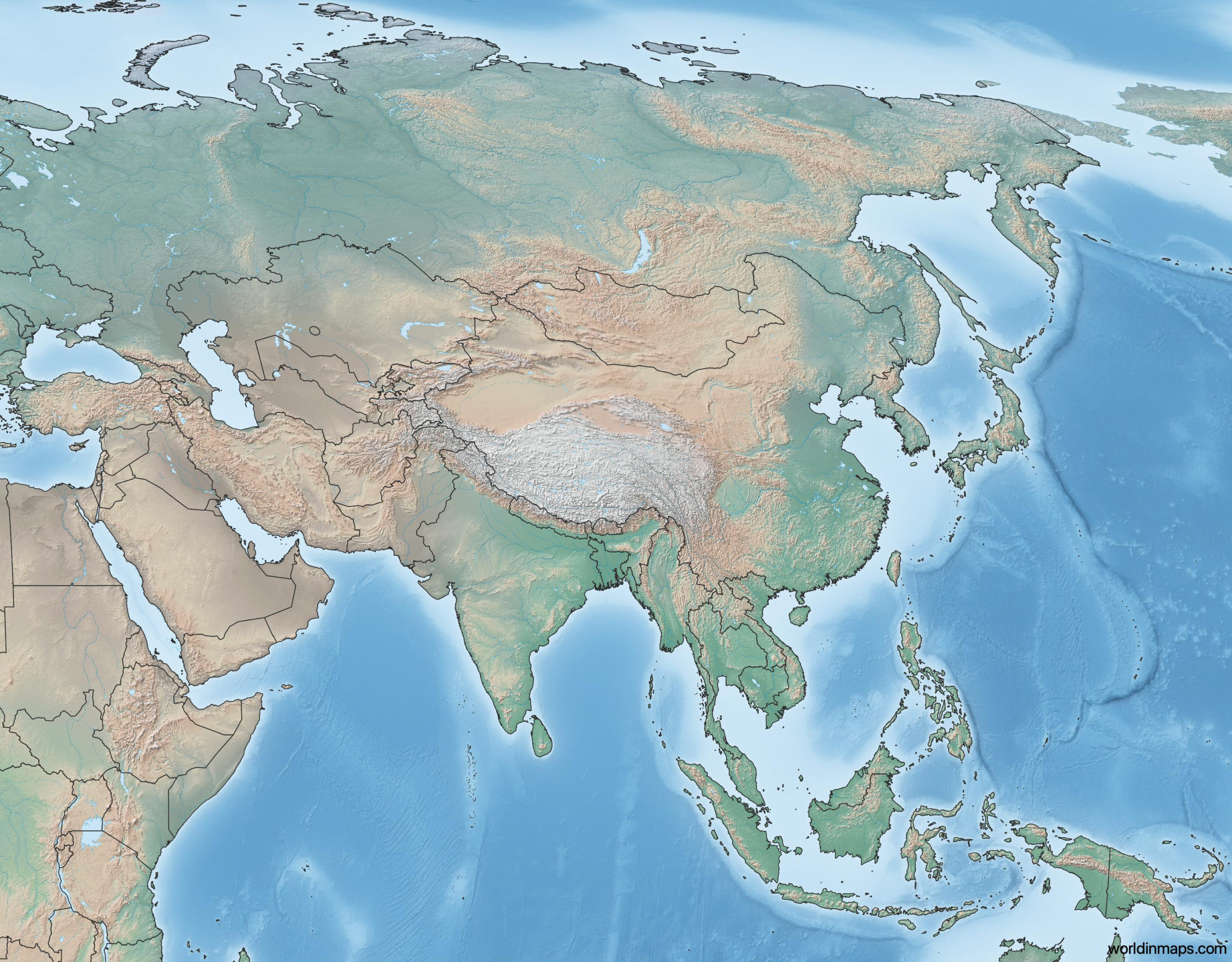
Asia’s topography is a story told in dramatic relief. The continent is dominated by a vast central plateau, the "Roof of the World," known as the Tibetan Plateau. This plateau, with its average elevation exceeding 4,000 meters, acts as a geographic pivot, giving rise to a series of towering mountain ranges that radiate outwards.
-
The Himalayas: This majestic mountain range, home to the world’s highest peak, Mount Everest, forms a formidable barrier between the Indian subcontinent and the rest of Asia. Its towering peaks and deep valleys have profound implications for climate, biodiversity, and human settlement patterns.
-
The Hindu Kush: This range, extending westward from the Himalayas, stretches through Afghanistan and Pakistan, playing a significant role in shaping regional climates and influencing cultural interactions.
-
The Tian Shan: This massive mountain system, located in Central Asia, serves as a natural boundary between China and Kazakhstan, with its snow-capped peaks and glaciers contributing to regional water resources.
-
The Altai Mountains: This range, spanning Russia, Mongolia, China, and Kazakhstan, is known for its rugged terrain and diverse ecosystems, including alpine meadows, forests, and steppes.
-
The Caucasus Mountains: Located between the Black and Caspian Seas, this range is characterized by its volcanic peaks and lush valleys, harboring a diverse array of flora and fauna.
Beyond the mountains, Asia’s landscape is further sculpted by vast plains, expansive deserts, and fertile river valleys.
-
The Great Plains of China: This vast expanse of fertile land, stretching from the eastern coast to the Tibetan Plateau, has been a cradle of civilization for millennia, supporting a dense population and intensive agricultural activities.
-
The Siberian Plain: This immense region in northern Asia is characterized by its flat terrain and harsh climate, supporting vast taiga forests and tundra ecosystems.
-
The Arabian Peninsula: Home to the world’s largest sand desert, the Rub’ al Khali, this region is defined by its arid landscape and sparse vegetation, presenting unique challenges for human habitation.
-
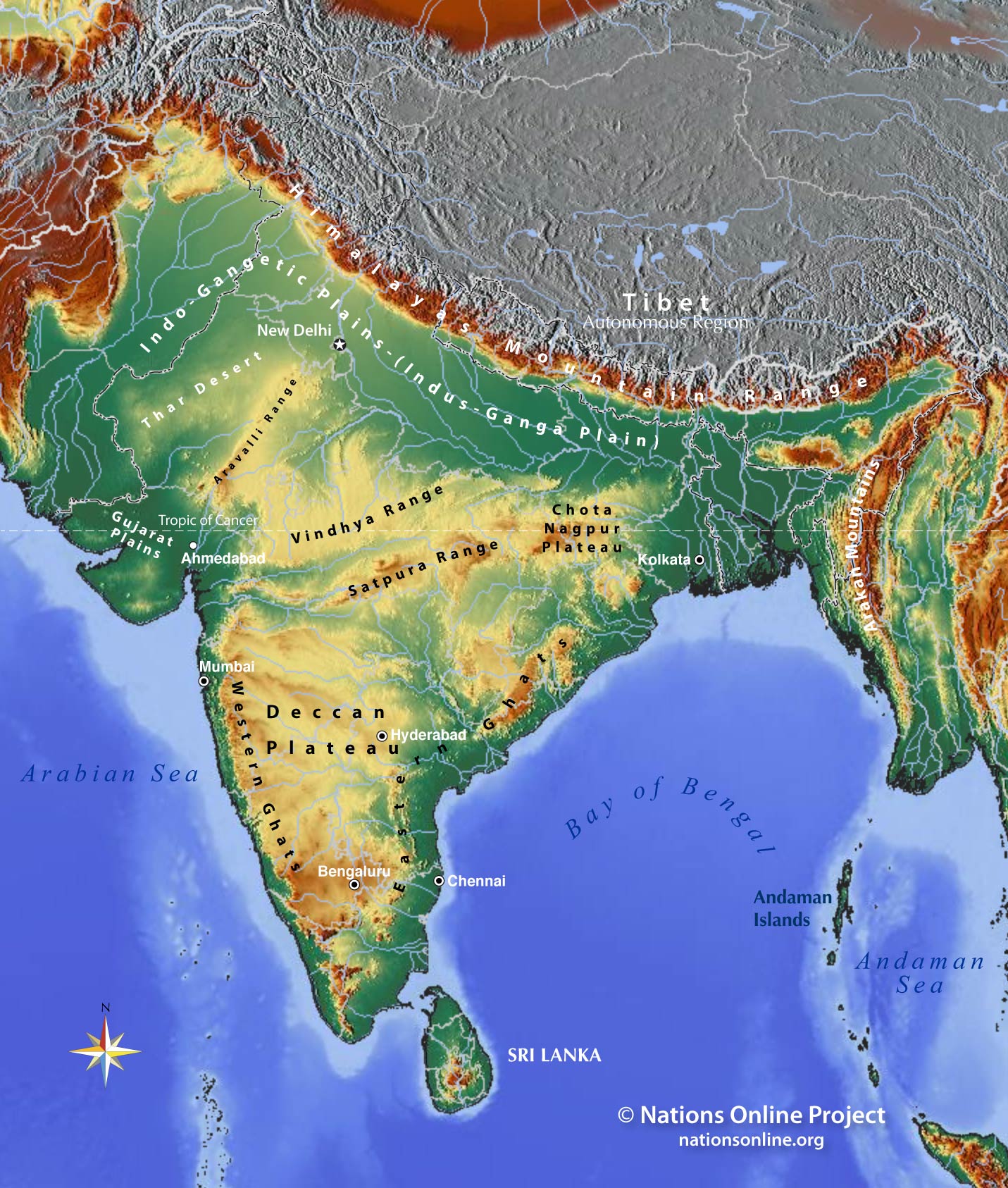
The Indus River Valley: This fertile region in Pakistan and India, nourished by the Indus River, has been a center of civilization for thousands of years, supporting agriculture and urban development.
-
The Mekong Delta: This vast delta, formed by the Mekong River in Vietnam, is a fertile agricultural region, renowned for its rice production and vibrant waterways.
Topographical Maps: Unlocking the Secrets of Asia’s Landscape
Topographical maps, with their intricate lines and symbols, provide a crucial tool for understanding the complex interplay of these diverse features. They depict not only the elevation and shape of the land but also the distribution of rivers, lakes, forests, and other natural features.
-
Contour Lines: These lines connect points of equal elevation, providing a visual representation of the terrain’s slope and form. They allow for the identification of mountains, valleys, plateaus, and other topographical features.
-
Spot Heights: These markers indicate the exact elevation of specific points on the map, offering precise measurements of the terrain’s verticality.
-
Rivers and Lakes: These features are depicted with blue lines and symbols, highlighting the flow of water and the presence of major bodies of water.
-
Forests and Vegetation: Green areas on topographical maps indicate the presence of forests, while other symbols represent different types of vegetation, providing insights into the distribution of plant life.
-
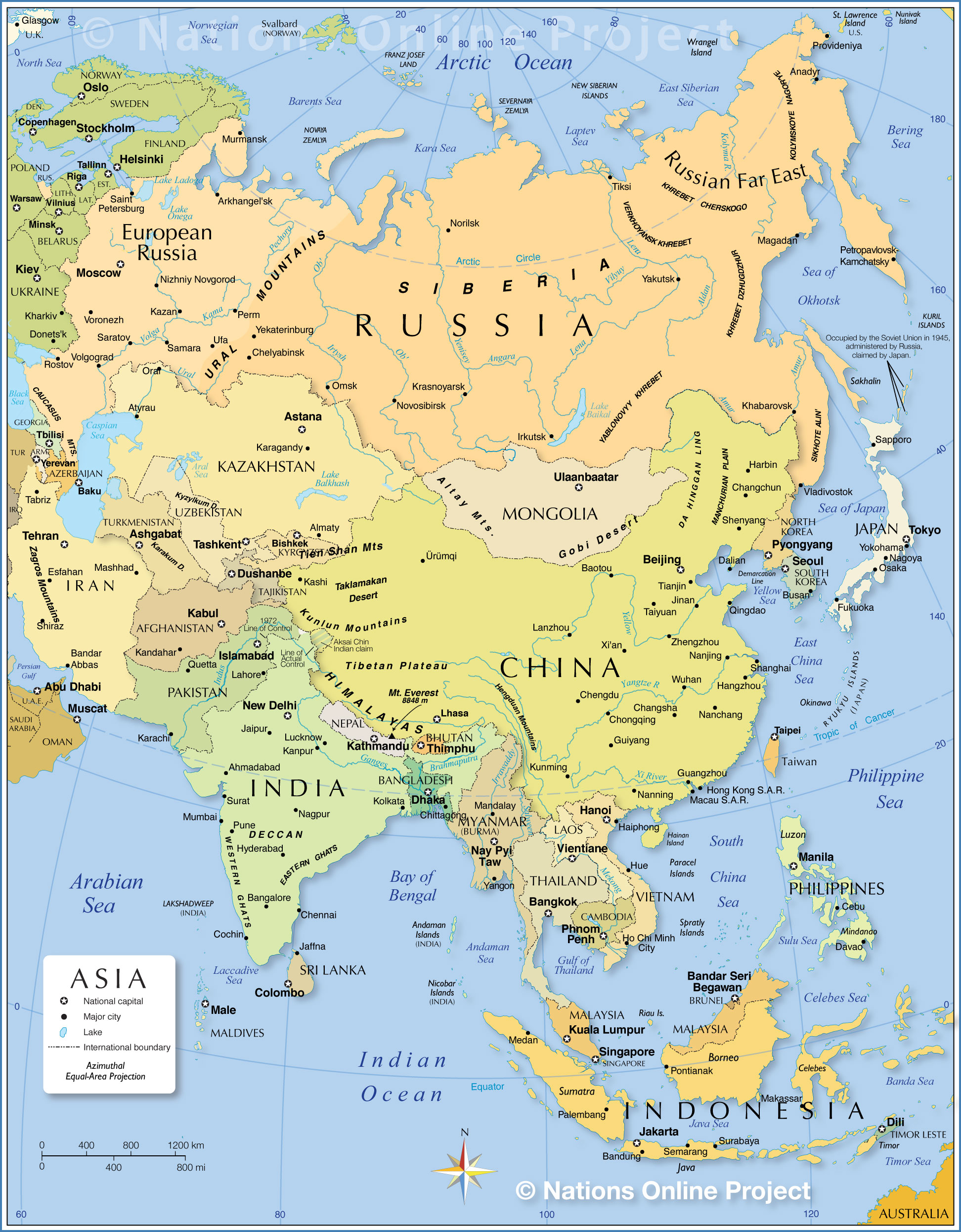
Settlements and Infrastructure: Topographical maps often include symbols representing cities, towns, roads, and other infrastructure, providing context for human activities within the landscape.
The Importance of Topographical Maps in Understanding Asia
Topographical maps play a crucial role in understanding the complexities of Asia’s diverse landscape, contributing to various fields of study and practical applications.
-
Geography and Geology: Topographical maps provide essential data for understanding the formation of mountain ranges, the flow of rivers, the distribution of geological formations, and the impact of tectonic activity.
-
Climate and Weather: The elevation, slope, and orientation of the terrain influence local climates and weather patterns, impacting rainfall, temperature, and wind patterns. Topographical maps provide crucial insights for understanding these climatic variations.
-
Ecology and Biodiversity: The diverse topography of Asia supports a wide range of ecosystems, from alpine meadows to tropical rainforests. Topographical maps help identify these ecosystems, understand their interconnectedness, and assess the impact of human activities on biodiversity.
-
Human Geography and Development: The distribution of mountains, rivers, and plains influences patterns of human settlement, agricultural practices, transportation routes, and economic development. Topographical maps provide a framework for understanding these human-environment interactions.
-
Resource Management and Conservation: Topographical maps are essential tools for managing natural resources, including water, forests, and minerals. They assist in identifying areas of ecological importance, planning conservation efforts, and mitigating the impact of human activities.
-
Disaster Preparedness and Response: Understanding the topography of a region is crucial for predicting and mitigating natural disasters, such as earthquakes, landslides, floods, and droughts. Topographical maps provide valuable data for disaster preparedness planning and response efforts.
FAQs about Topographical Maps of Asia
1. What are the different types of topographical maps available for Asia?
Topographical maps of Asia are available in various scales and formats, ranging from large-scale maps depicting specific regions to smaller-scale maps showing the entire continent. These maps can be printed, digital, or online, and they may focus on specific features like elevation, vegetation, or human settlements.
2. How can I access and use topographical maps of Asia?
Topographical maps of Asia are widely available online through government agencies, research institutions, and mapping services. You can also find printed maps at bookstores and specialty map retailers.
3. What are some of the challenges in creating and using topographical maps of Asia?
Creating accurate topographical maps of Asia presents challenges due to its vast size, diverse terrain, and often inaccessible areas. Data acquisition, especially in remote regions, can be challenging, requiring specialized equipment and techniques.
4. How do topographical maps contribute to understanding the relationship between humans and the environment in Asia?
Topographical maps provide insights into the distribution of natural resources, the influence of terrain on human settlements, and the impact of human activities on the environment. They help us understand the complex interplay between humans and their surroundings, informing sustainable development and resource management practices.
5. What are some future directions for the use of topographical maps in Asia?
Advances in technology, such as remote sensing and Geographic Information Systems (GIS), are transforming the creation and use of topographical maps. These tools are enabling the development of more detailed and accurate maps, facilitating a deeper understanding of Asia’s diverse landscape and its implications for human activities.
Tips for Using Topographical Maps of Asia
-
Understand the map’s scale and projection: The scale determines the level of detail and the area covered by the map. The projection defines how the Earth’s spherical surface is represented on a flat map.
-
Identify key features: Familiarize yourself with the symbols and conventions used on the map, including contour lines, spot heights, rivers, lakes, and other features.
-
Analyze the terrain: Use contour lines to understand the slope, elevation, and form of the land. Identify mountain ranges, valleys, plateaus, and other topographical features.
-
Relate the topography to human activities: Consider how the terrain influences human settlements, transportation routes, agricultural practices, and economic development.
-
Use the map in conjunction with other data: Combine topographical maps with other data sources, such as climate data, population statistics, or satellite imagery, to gain a comprehensive understanding of the region.
Conclusion
Topographical maps serve as indispensable tools for understanding the intricate and diverse landscape of Asia. They provide a visual key to deciphering the continent’s complex topography, its ecological systems, and the human civilizations that have thrived within its boundaries. By exploring the intricate lines and symbols of topographical maps, we gain a deeper appreciation for Asia’s unique geographical character and the interconnectedness of its natural and human systems. As technology continues to advance, topographical maps will continue to play a vital role in informing research, development, and decision-making across various fields, contributing to a more sustainable and informed future for Asia.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Topographical Journey Through Asia: Unveiling the Land’s Diverse Landscape. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!