East Jerusalem: A City Divided, A Map Of Contention
By admin / September 22, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
East Jerusalem: A City Divided, A Map of Contention
Related Articles: East Jerusalem: A City Divided, A Map of Contention
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to East Jerusalem: A City Divided, A Map of Contention. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
East Jerusalem: A City Divided, A Map of Contention

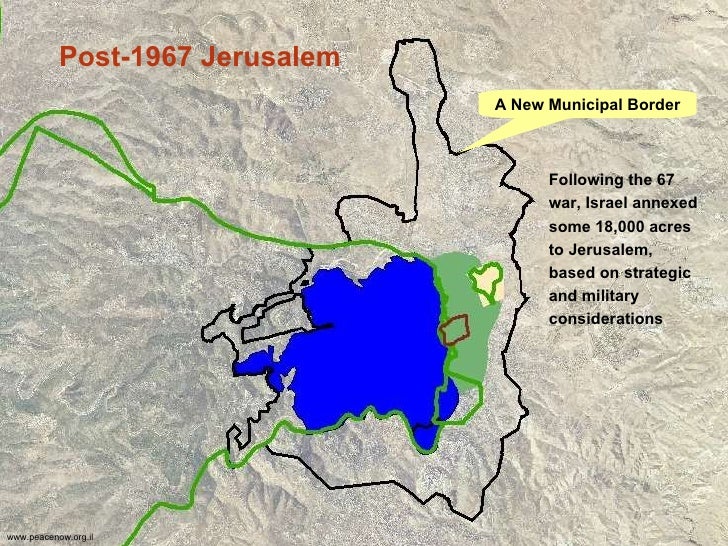
The map of East Jerusalem, a complex tapestry of history, culture, and politics, remains a central point of contention in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. This area, captured by Israel in the 1967 Six-Day War and later annexed, holds profound significance for both Israelis and Palestinians, making its cartographic representation a subject of intense debate and scrutiny.
A Historical Perspective:
East Jerusalem, encompassing the Old City and surrounding neighborhoods, has been a focal point of human activity for millennia. Its strategic location, nestled within the Judean Hills, has attracted empires and civilizations, each leaving their mark on its landscape and identity. From the Roman conquest to the Ottoman Empire, the city has witnessed periods of prosperity and decline, reflecting the shifting tides of power in the region.
The 1967 War and its Aftermath:
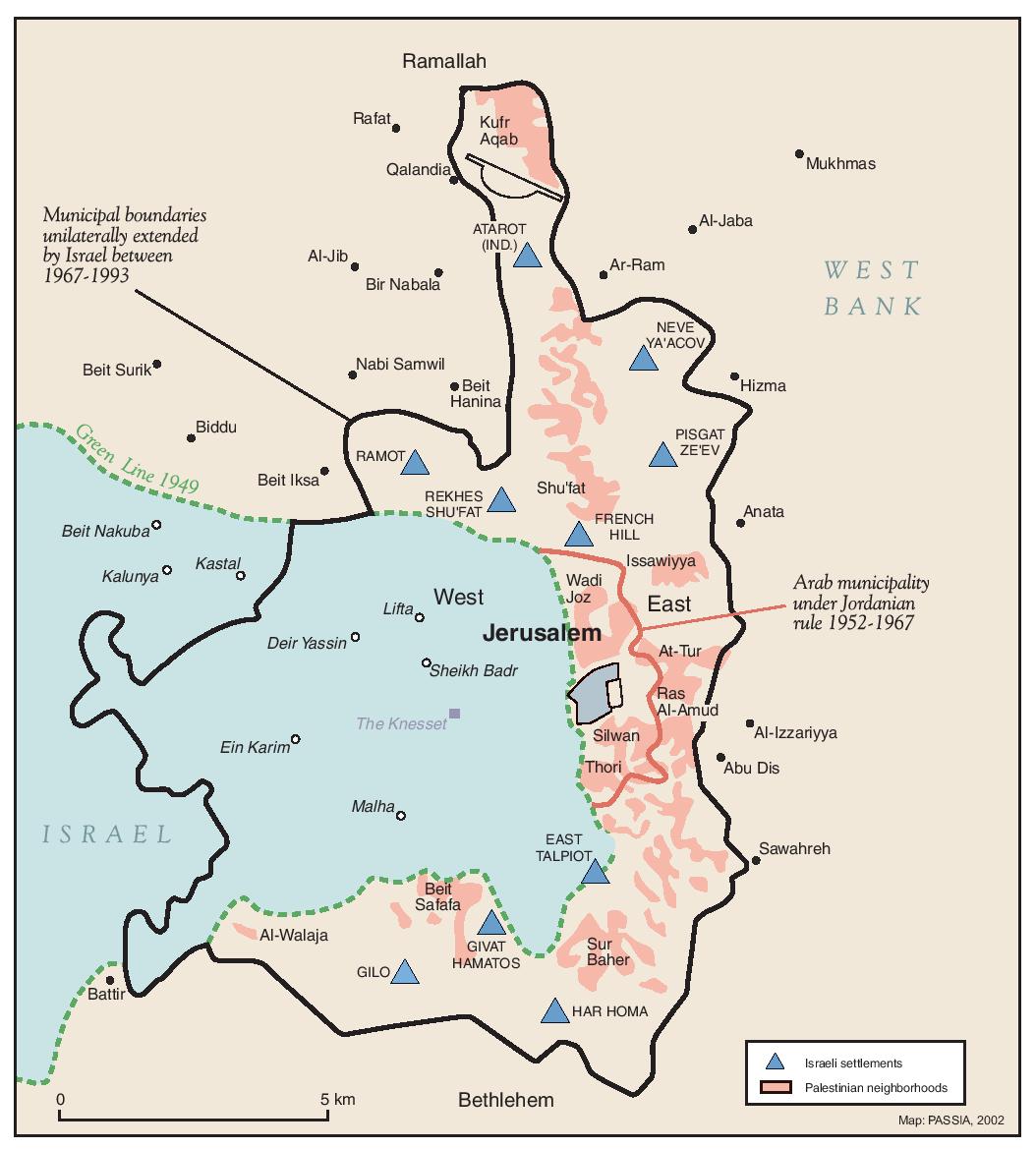
The 1967 Six-Day War marked a turning point in East Jerusalem’s history. Following the Israeli victory, Israel annexed East Jerusalem, extending its municipal boundaries and claiming the entire city as its unified capital. This move, however, was met with international condemnation and remains unrecognized by the international community. The Palestinians, who view East Jerusalem as the capital of their future state, consider the annexation illegal and a violation of their rights.
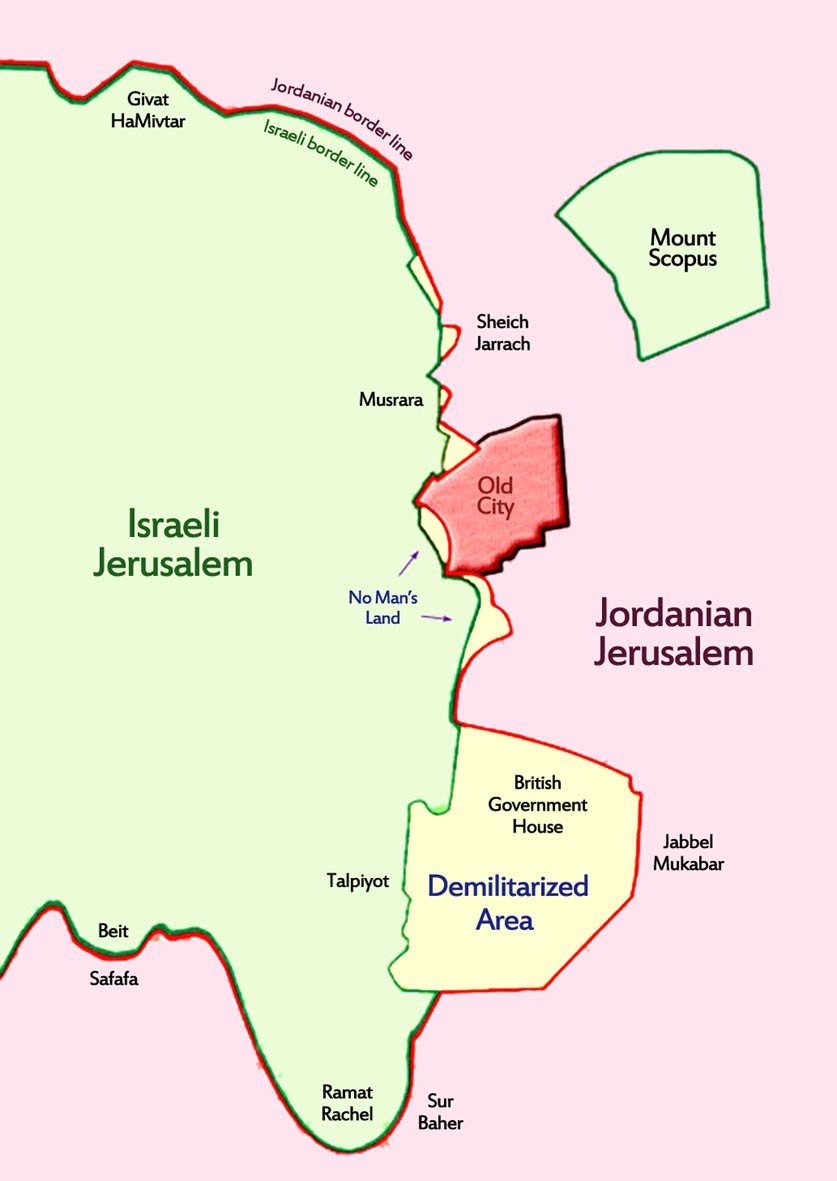
The Map of East Jerusalem: A Visual Representation of Conflict:
The map of East Jerusalem, often depicted in different ways depending on the perspective, serves as a visual representation of the complex geopolitical realities at play.
- Israeli Perspective: The map typically portrays East Jerusalem as an integral part of the unified city of Jerusalem, highlighting its historical and religious significance to Judaism.
- Palestinian Perspective: The map often depicts East Jerusalem as a distinct entity, separate from West Jerusalem, emphasizing its importance as the future capital of a Palestinian state.
The differing interpretations of the map reflect the conflicting narratives surrounding East Jerusalem, highlighting the deep chasm between the two sides.
Beyond the Map: The Human Cost of Conflict:
The map of East Jerusalem, while a crucial visual element in understanding the conflict, cannot fully encapsulate the human cost of the ongoing dispute. The city is home to a diverse population of Jews, Muslims, Christians, and Armenians, each with their own unique history and cultural heritage. The conflict has resulted in displacement, segregation, and limited access to resources, creating a complex social and economic landscape.
Key Points of Contention:
The map of East Jerusalem, while a visual representation, is also a reflection of the following key points of contention:
- Jerusalem’s Status: The status of Jerusalem, particularly East Jerusalem, remains the most contentious issue in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. Both sides claim the city as their capital, leading to ongoing tensions and disputes.
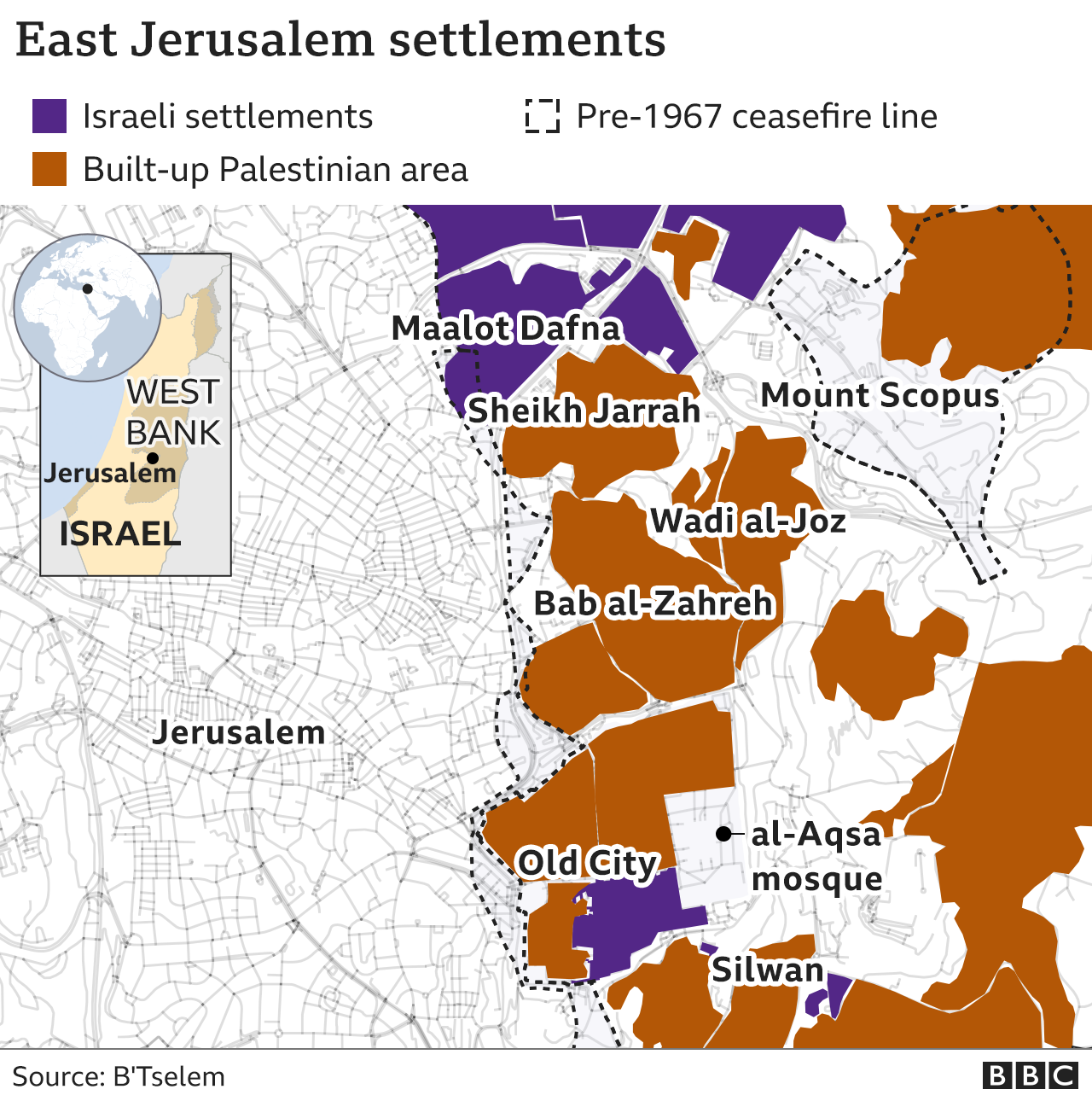
- Settlements: Israeli settlements, located in East Jerusalem and the surrounding West Bank, are considered illegal under international law. Their presence further exacerbates the conflict, as they are seen as obstacles to a two-state solution.
- Access to Holy Sites: The Old City of Jerusalem, located in East Jerusalem, is home to holy sites revered by Jews, Muslims, and Christians. The control over these sites, particularly the Temple Mount (Al-Aqsa Mosque compound), is a constant source of friction and potential conflict.
- Palestinian Rights: The Palestinian population in East Jerusalem faces numerous challenges, including limited access to basic services, restrictions on movement, and discriminatory policies. The map of East Jerusalem reflects the ongoing struggle for Palestinian rights and self-determination.
FAQs on the Map of East Jerusalem:
Q: What is the significance of the Old City of Jerusalem?
A: The Old City of Jerusalem, located within East Jerusalem, holds immense religious and historical significance for Jews, Muslims, and Christians. It is home to the Western Wall, the Temple Mount (Al-Aqsa Mosque compound), the Church of the Holy Sepulchre, and other sacred sites.
Q: Why is East Jerusalem considered a disputed territory?
A: East Jerusalem was captured by Israel in the 1967 Six-Day War and subsequently annexed. This annexation is not recognized by the international community, and Palestinians consider it illegal and a violation of their rights.
Q: What are the implications of the Israeli settlements in East Jerusalem?
A: The Israeli settlements, located in East Jerusalem and the surrounding West Bank, are considered illegal under international law. They are seen as obstacles to a two-state solution and further exacerbate the conflict.
Q: What are the challenges faced by Palestinians in East Jerusalem?
A: Palestinians in East Jerusalem face numerous challenges, including limited access to basic services, restrictions on movement, and discriminatory policies. They also struggle with the ongoing threat of displacement and the erosion of their cultural identity.
Tips for Understanding the Map of East Jerusalem:
- Consult multiple sources: Examine maps from various perspectives, including Israeli, Palestinian, and international organizations, to gain a broader understanding of the different interpretations and contested areas.
- Consider historical context: Research the history of East Jerusalem, particularly the events leading up to and following the 1967 Six-Day War, to grasp the complexities of the current situation.
- Understand the political landscape: Familiarize yourself with the positions of key players, including Israel, Palestine, and the international community, to gain insight into the ongoing negotiations and disputes.
- Engage with diverse perspectives: Seek out perspectives from both Israelis and Palestinians, as well as international observers, to understand the multifaceted nature of the conflict.
Conclusion:
The map of East Jerusalem serves as a visual representation of a complex and multifaceted conflict. Understanding its historical context, geopolitical significance, and the diverse perspectives surrounding it is crucial for navigating the ongoing dispute. While the map itself cannot fully encapsulate the human cost of the conflict, it offers a valuable tool for analyzing the ongoing struggle for peace and justice in the region.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into East Jerusalem: A City Divided, A Map of Contention. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!