Mapping The Vanishing Ice: A Visual Guide To Climate Change
By admin / May 18, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Mapping the Vanishing Ice: A Visual Guide to Climate Change
Related Articles: Mapping the Vanishing Ice: A Visual Guide to Climate Change
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Vanishing Ice: A Visual Guide to Climate Change. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Vanishing Ice: A Visual Guide to Climate Change
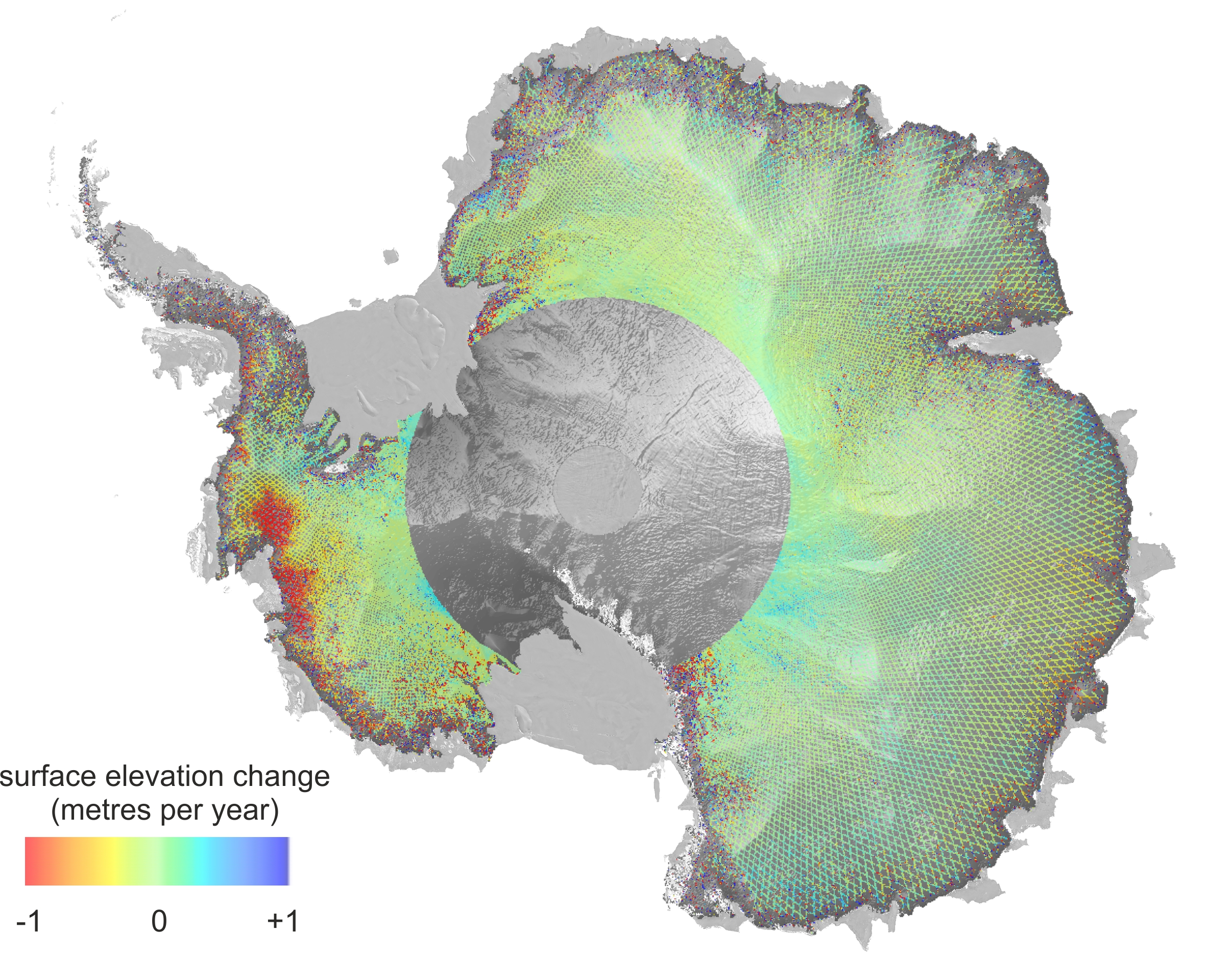
The Earth’s polar regions are experiencing a dramatic transformation, with ice caps and glaciers melting at an unprecedented rate. This phenomenon, driven by global warming, is not merely a distant environmental concern; it holds profound implications for the planet’s ecosystems, human societies, and the future of our climate. Understanding the scope and impact of melting ice requires a visual representation, a tool that allows us to grasp the magnitude of this change and its far-reaching consequences.
Visualizing the Melt:
The concept of a "melting ice caps map" encompasses a variety of data visualizations that depict the shrinking ice cover in both the Arctic and Antarctic. These maps can take various forms, from simple satellite images highlighting areas of ice loss to complex, interactive platforms that showcase historical trends, projected future scenarios, and the associated environmental and societal impacts.
Key Features of a Melting Ice Caps Map:
- Geographic Representation: The map visually represents the polar regions, highlighting the extent of ice cover in both the Arctic and Antarctic.
- Temporal Data: The map incorporates data from different time periods, enabling the visualization of ice loss over time. This temporal perspective demonstrates the rate of change and its acceleration.
- Data Overlay: The map can overlay various data layers, such as sea level rise projections, changes in sea ice thickness, and the location of vulnerable coastal communities. This multi-layered approach provides a comprehensive understanding of the interconnectedness of climate change impacts.
- Interactive Features: Many melting ice caps maps are interactive, allowing users to zoom in on specific regions, explore data points, and access detailed information about the melting process and its effects.
Benefits of a Melting Ice Caps Map:
- Raising Awareness: Maps serve as powerful tools for communicating complex scientific data to a wider audience. By visualizing the magnitude of ice loss, they effectively raise awareness about the urgency of climate change and its consequences.
- Policy Support: Maps provide visual evidence of the accelerating ice melt, supporting the need for policy changes and international collaboration to mitigate climate change and adapt to its impacts.
- Scientific Research: Maps are essential for scientific research, allowing researchers to track changes in ice cover, analyze trends, and develop models to predict future scenarios.
- Education and Outreach: Maps can be used in educational settings to teach students about climate change and its impacts, fostering a deeper understanding of the issue.
Understanding the Data:
Melting ice caps maps rely on data collected from various sources, including:
- Satellite Imagery: Satellites continuously monitor the polar regions, providing high-resolution images that capture changes in ice cover over time.
- Ice Thickness Measurements: Instruments mounted on satellites and airplanes measure the thickness of ice sheets and glaciers, providing crucial data on their volume and stability.
- Climate Models: Computer models simulate the Earth’s climate system, incorporating data on factors like temperature, precipitation, and ice dynamics to project future scenarios of ice melt.
Beyond the Visual:
While maps are essential for visualizing the changes in ice cover, they are only part of the story. It is crucial to understand the underlying processes driving the melt and the consequences of this phenomenon.
The Drivers of Ice Melt:
- Rising Global Temperatures: The primary driver of ice melt is the increase in global temperatures due to greenhouse gas emissions. This warming effect melts ice directly and also alters the physical properties of ice, making it more susceptible to melting.
- Ocean Warming: Ocean temperatures are also rising, contributing to the melting of glaciers and ice shelves from below. Warmer ocean waters melt ice faster and also destabilize ice shelves, causing them to break apart.
- Changes in Precipitation Patterns: Altered precipitation patterns can lead to increased snowfall in some areas, but the overall trend is towards reduced snowfall and a decrease in ice accumulation.
Consequences of Ice Melt:
- Sea Level Rise: As ice caps and glaciers melt, the water flows into the oceans, causing sea levels to rise. This poses a significant threat to coastal communities, infrastructure, and ecosystems.
- Disruption of Ecosystems: Melting ice disrupts the delicate balance of polar ecosystems, affecting the habitats of animals like polar bears, seals, and penguins.
- Changes in Ocean Circulation: Melting ice influences ocean currents, potentially altering global weather patterns and impacting marine ecosystems.
- Release of Methane: As permafrost thaws due to rising temperatures, it releases methane, a potent greenhouse gas, further exacerbating climate change.
FAQs:
1. Why are ice caps melting?
Ice caps are melting primarily due to rising global temperatures caused by human-induced climate change. This warming effect melts ice directly and also alters the physical properties of ice, making it more susceptible to melting.
2. What is the impact of melting ice caps on sea level rise?
Melting ice caps contribute significantly to sea level rise. As ice melts, the water flows into the oceans, increasing their volume and causing sea levels to rise. This poses a significant threat to coastal communities, infrastructure, and ecosystems.
3. How can we prevent ice caps from melting?
Preventing further ice melt requires a global effort to reduce greenhouse gas emissions through transitioning to renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and implementing sustainable practices.
4. Are there any solutions to address the consequences of ice melt?
Addressing the consequences of ice melt requires a combination of adaptation and mitigation strategies. Adaptation measures include building sea walls, relocating coastal communities, and developing drought-resistant crops. Mitigation strategies focus on reducing greenhouse gas emissions and slowing down the rate of climate change.
5. How can I contribute to combating ice melt?
You can contribute to combating ice melt by reducing your carbon footprint through actions such as:
- Conserving energy: Turn off lights when you leave a room, use energy-efficient appliances, and consider installing solar panels.
- Reducing transportation emissions: Walk, bike, or use public transportation instead of driving alone.
- Consuming sustainably: Choose products with less packaging, reduce food waste, and support businesses that prioritize sustainability.
- Advocating for change: Engage in political action, support environmental organizations, and educate others about the importance of addressing climate change.
Tips for Using Melting Ice Caps Maps:
- Focus on the message: Emphasize the visual impact of the data to drive home the urgency of the issue.
- Provide context: Explain the data presented on the map, including the time frame, the data sources, and the significance of the changes observed.
- Highlight key regions: Draw attention to specific areas experiencing significant ice loss and the potential consequences for those regions.
- Connect the dots: Show how melting ice caps are linked to other environmental and societal challenges, such as sea level rise, coastal erosion, and climate change impacts on human populations.
- Encourage action: Use the map to inspire action and empower individuals to contribute to mitigating climate change.
Conclusion:
Melting ice caps maps are powerful tools for visualizing the dramatic changes occurring in the Earth’s polar regions. By presenting data on ice loss in a clear and accessible format, these maps raise awareness, support policy decisions, and foster a deeper understanding of the urgency of addressing climate change. While the maps offer a glimpse into the reality of a changing planet, it is crucial to remember that they represent only a part of the story. Addressing this global challenge requires a comprehensive understanding of the complex processes driving ice melt, the far-reaching consequences of this phenomenon, and the urgent need for collective action to mitigate climate change and adapt to its impacts.







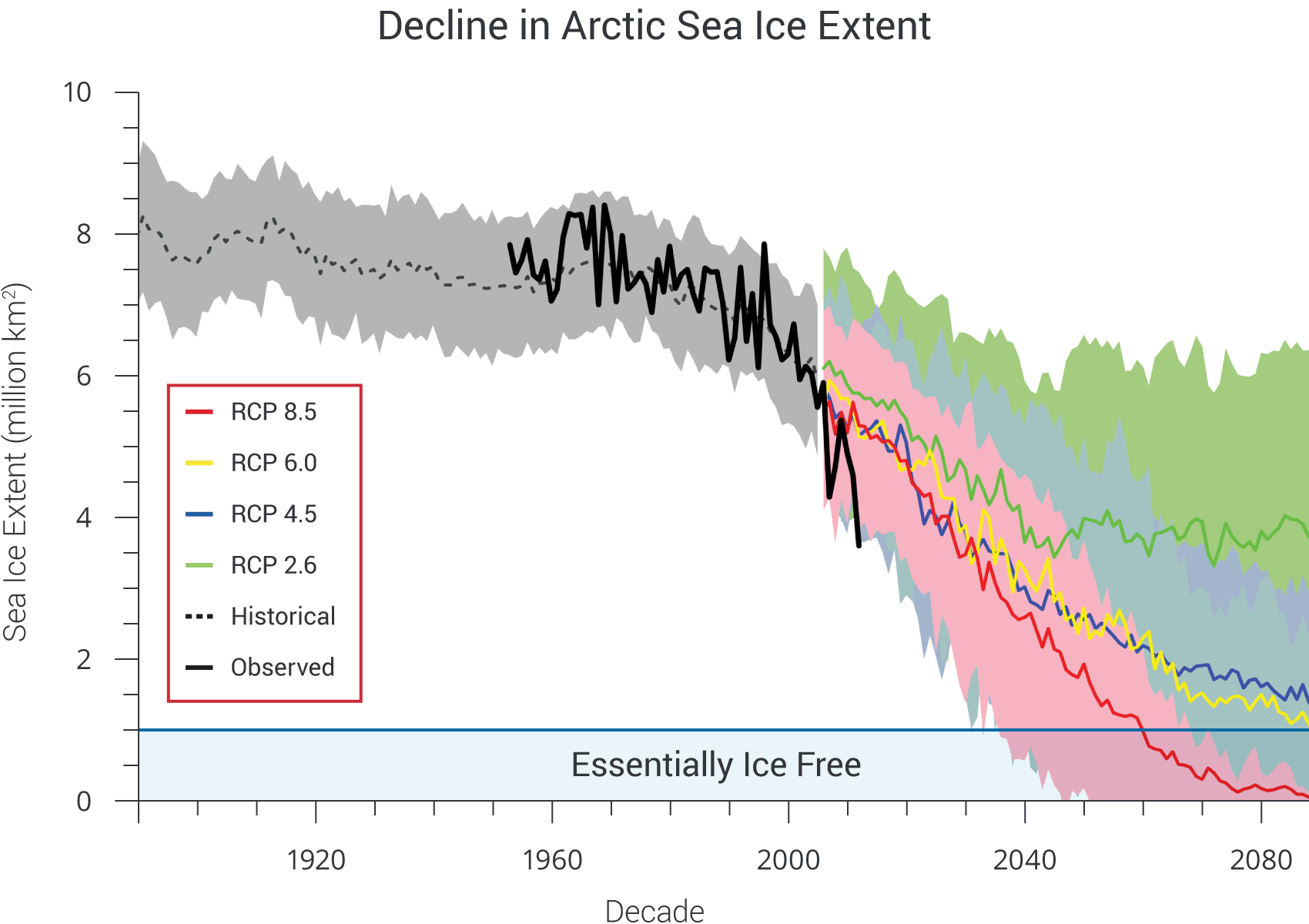
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Vanishing Ice: A Visual Guide to Climate Change. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!