Mapping West Bengal: A Comprehensive Guide To The State’s Geographic Tapestry
By admin / June 12, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Mapping West Bengal: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Geographic Tapestry
Related Articles: Mapping West Bengal: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Geographic Tapestry
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Mapping West Bengal: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Geographic Tapestry. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping West Bengal: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Geographic Tapestry
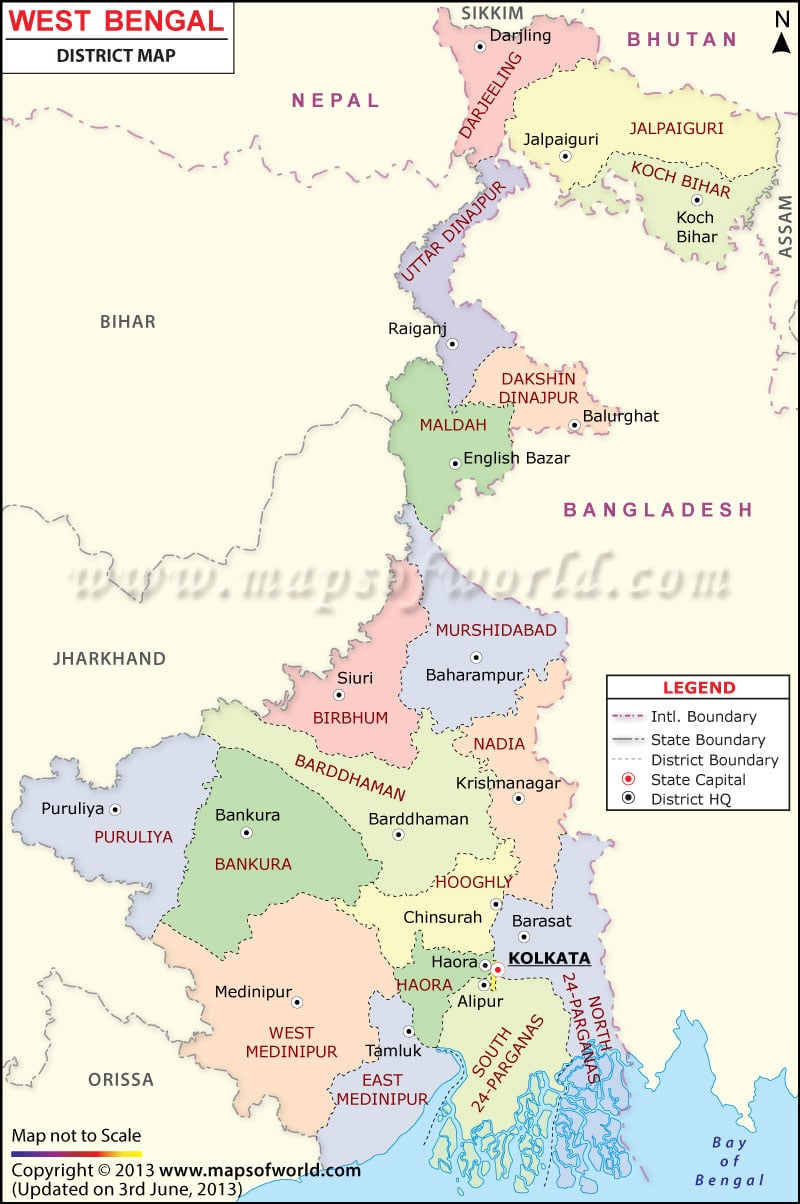
West Bengal, a state in eastern India, is a vibrant tapestry of diverse landscapes, rich cultural heritage, and a dynamic population. Understanding its geography is crucial for appreciating its unique character and navigating its complexities. Maps serve as invaluable tools for visualizing this intricate web of physical and human features, providing insights into the state’s topography, resources, infrastructure, and socio-economic dynamics.
The Physical Landscape: A Tapestry of Terrain
West Bengal’s physical landscape is marked by a remarkable diversity, ranging from the fertile plains of the Gangetic delta to the rugged hills of the Himalayas. The state is divided into three major physiographic regions:
-
The Gangetic Plains: Covering the majority of West Bengal, these plains are characterized by fertile alluvial soil deposited by the Ganges and Brahmaputra rivers. They are home to dense agricultural land, bustling cities, and a significant portion of the state’s population. The plains are crisscrossed by numerous rivers, including the Hooghly, Damodar, and Bhagirathi, providing vital irrigation and transportation networks.
-
The Himalayan Foothills: The northern boundary of West Bengal is marked by the foothills of the Himalayas, including the Darjeeling and Sikkim Himalayas. These regions are known for their stunning natural beauty, including lush forests, snow-capped peaks, and diverse wildlife. They are also home to tea plantations, which are a vital part of the state’s economy.
-
The Sundarbans: Located in the southern part of West Bengal, the Sundarbans is the world’s largest mangrove forest, a UNESCO World Heritage site. This unique ecosystem is characterized by its dense mangrove vegetation, rich biodiversity, and intricate network of tidal channels. The Sundarbans is also home to the Royal Bengal Tiger, a flagship species that symbolizes the region’s ecological significance.
Mapping Resources: Unveiling the State’s Wealth
West Bengal boasts a rich endowment of natural resources, crucial for its economic development and well-being. Maps play a vital role in understanding the distribution and potential of these resources, aiding in efficient resource management and sustainable development.
-
Water Resources: The state’s abundant river systems, including the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and their tributaries, provide a vital source of water for irrigation, drinking, and industrial use. Maps help identify potential water sources, assess their availability, and plan for efficient water management strategies, mitigating the risk of water scarcity in densely populated areas.
-
Mineral Resources: West Bengal is home to a variety of mineral deposits, including coal, limestone, iron ore, and bauxite. Maps are instrumental in mapping these deposits, identifying their potential for extraction, and guiding the development of mining industries. This helps ensure responsible resource extraction practices, minimizing environmental impact and maximizing economic benefits.
-
Forest Resources: The state’s forests, particularly in the Himalayan foothills and the Sundarbans, are vital for maintaining ecological balance, providing timber, and protecting biodiversity. Maps aid in monitoring forest cover, identifying areas prone to deforestation, and implementing conservation strategies to safeguard these vital ecosystems.
Infrastructure and Connectivity: Mapping a Network of Development
West Bengal’s infrastructure plays a crucial role in connecting its diverse regions, facilitating economic growth, and improving the quality of life for its citizens. Maps provide a visual representation of this infrastructure network, highlighting its strengths and weaknesses and guiding future development plans.
-
Transportation Network: The state’s transportation network encompasses roads, railways, waterways, and airports. Maps help visualize these networks, identify bottlenecks, and plan for infrastructure improvements, enhancing connectivity and facilitating trade and tourism.
-
Power Grid: Access to reliable electricity is vital for economic development and social progress. Maps help visualize the state’s power grid, identifying areas with inadequate access and guiding the expansion of power generation and distribution networks.
-
Communication Network: Effective communication is essential for information sharing, economic activity, and social interaction. Maps assist in mapping the state’s communication network, including telephone lines, internet infrastructure, and broadcasting facilities, identifying areas requiring improvement and guiding the development of a robust communication network.
Socio-economic Dynamics: Mapping the Human Landscape
West Bengal’s diverse population and complex socio-economic dynamics are reflected in its demographic patterns, economic activities, and social indicators. Maps provide valuable insights into these aspects, highlighting areas of development and potential for improvement.
-
Population Distribution: Maps illustrate the density and distribution of population across the state, highlighting urban centers, rural areas, and areas of high population growth. This information helps plan for infrastructure development, resource allocation, and social services to meet the needs of a growing population.
-
Economic Activities: Maps can depict the distribution of different economic activities, including agriculture, industry, and services, across the state. This information helps understand the economic landscape, identify areas of economic concentration, and guide policies for promoting balanced development.
-
Social Indicators: Maps can visualize the distribution of social indicators, such as literacy rates, health facilities, and access to basic amenities, across the state. This helps identify areas with high levels of deprivation and guide targeted interventions to address social inequalities and improve the quality of life for all citizens.
FAQs about Maps in West Bengal
Q: What types of maps are used in West Bengal?
A: West Bengal utilizes a variety of maps, including topographic maps, thematic maps, road maps, political maps, and satellite imagery. Each type of map serves a specific purpose, providing different insights into the state’s geography and socio-economic dynamics.
Q: How are maps used in planning and development in West Bengal?
A: Maps are indispensable tools for planning and development in West Bengal. They provide a visual representation of the state’s resources, infrastructure, and population distribution, helping identify areas for development, plan infrastructure projects, and allocate resources effectively.
Q: What are some of the challenges faced in using maps in West Bengal?
A: Challenges include data availability, accuracy, and accessibility. Ensuring the availability of accurate and up-to-date data is crucial for effective map-based planning and decision-making. Moreover, accessibility to maps and map-related technologies is essential for empowering individuals and organizations to utilize this valuable tool.
Q: How are maps used in disaster management in West Bengal?
A: Maps play a crucial role in disaster management, providing vital information about potential hazard zones, evacuation routes, and resource distribution. They help coordinate rescue and relief efforts, ensuring timely and efficient response to natural disasters.
Tips for Using Maps in West Bengal
-
Choose the right map for your purpose: Different maps serve different purposes. Select the map that provides the information you need, whether it’s a topographic map for understanding terrain, a thematic map for visualizing social indicators, or a road map for navigation.
-
Interpret the map carefully: Understand the symbols, legends, and scales used on the map to accurately interpret the information it presents.
-
Combine different maps: Combining different types of maps can provide a more comprehensive understanding of the region. For example, overlaying a population density map with a map of health facilities can help identify areas with a high population density and limited access to healthcare.
-
Utilize digital maps and GIS tools: Digital maps and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) offer advanced capabilities for data analysis, visualization, and spatial modeling. These tools can enhance the effectiveness of maps in planning, decision-making, and resource management.
Conclusion
Maps are essential tools for understanding the complex geography and socio-economic dynamics of West Bengal. They provide a visual representation of the state’s physical landscape, natural resources, infrastructure, and population distribution, aiding in planning, development, and decision-making. By utilizing maps effectively, individuals and organizations can gain valuable insights into the state’s strengths and weaknesses, promoting sustainable development and improving the lives of its citizens.
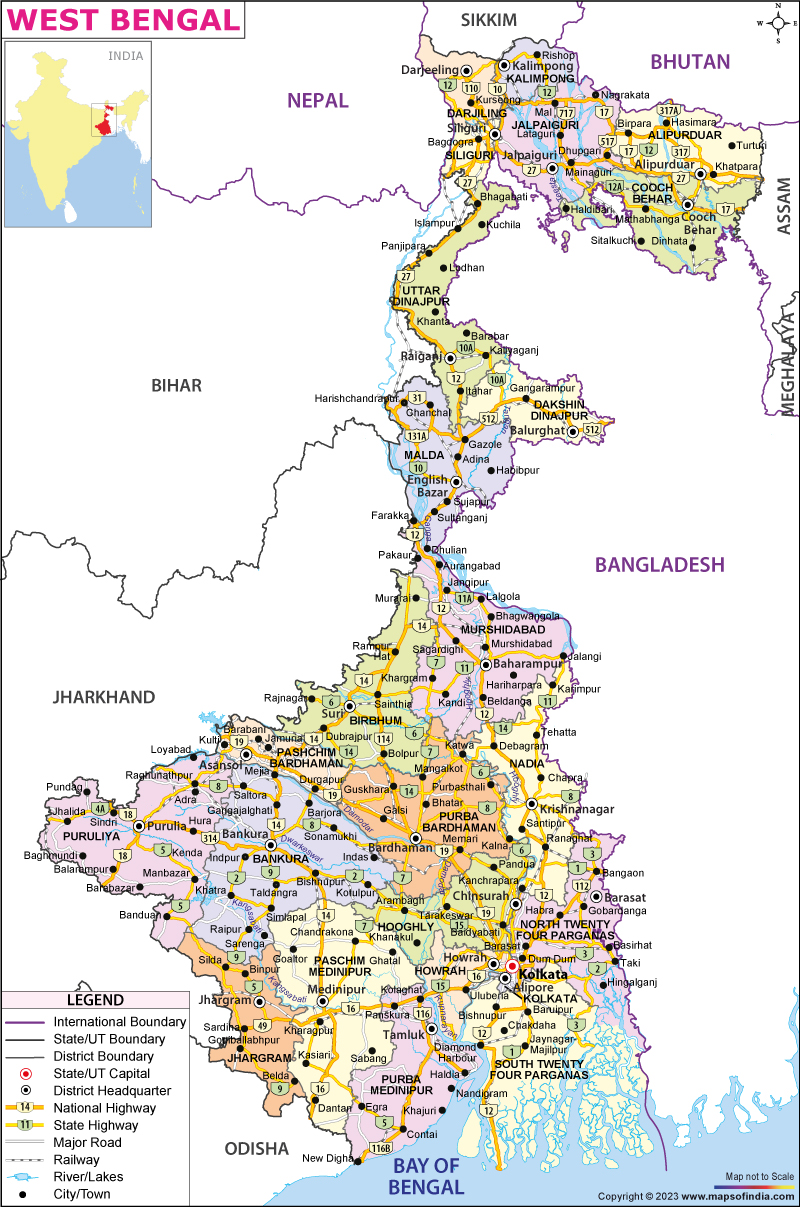
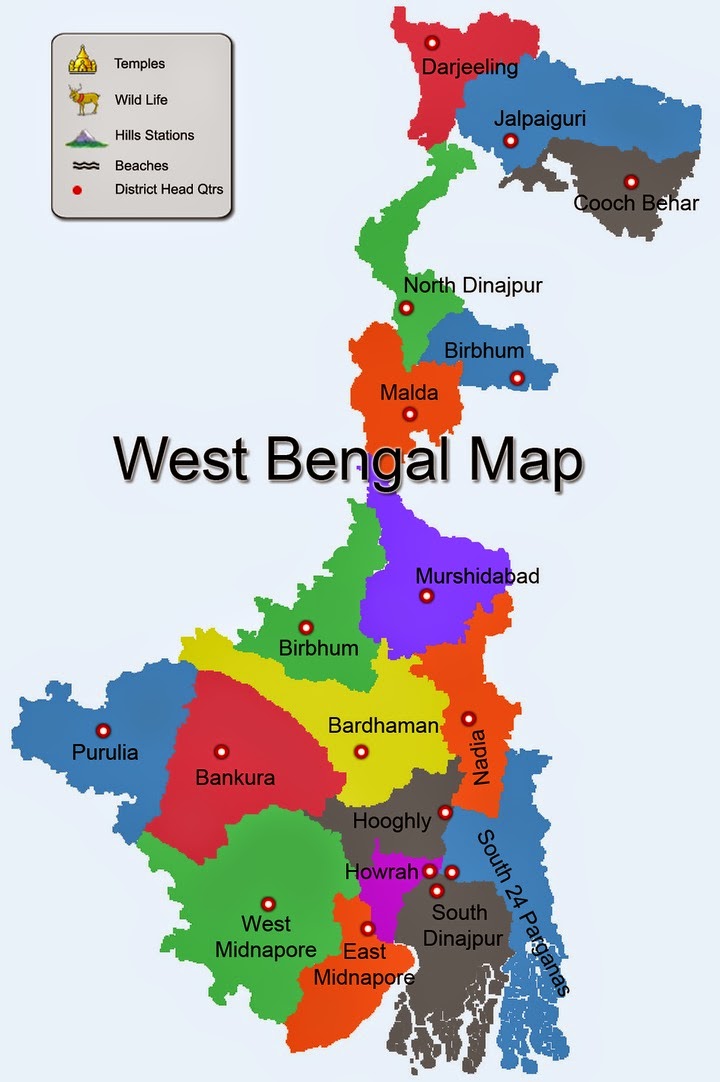
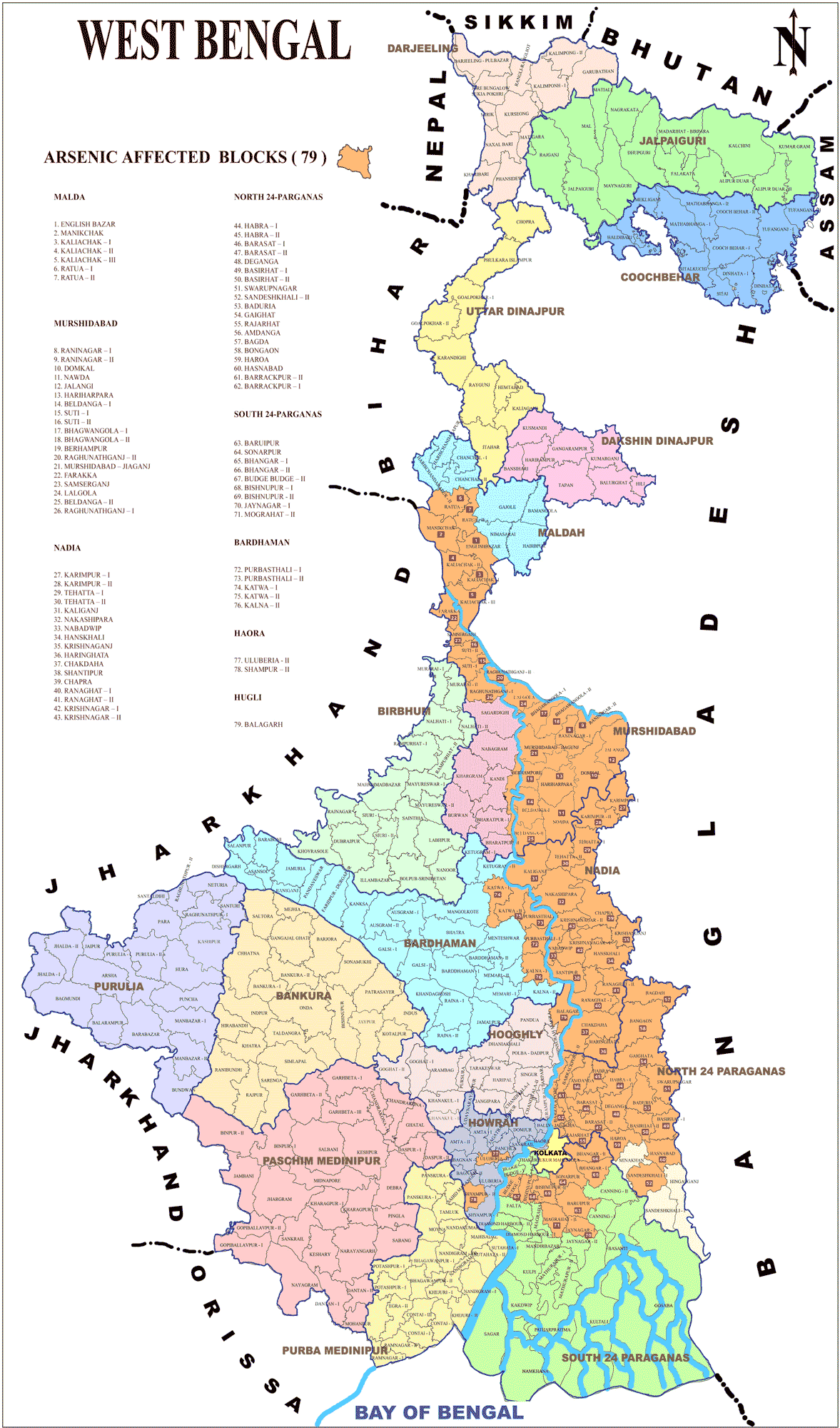



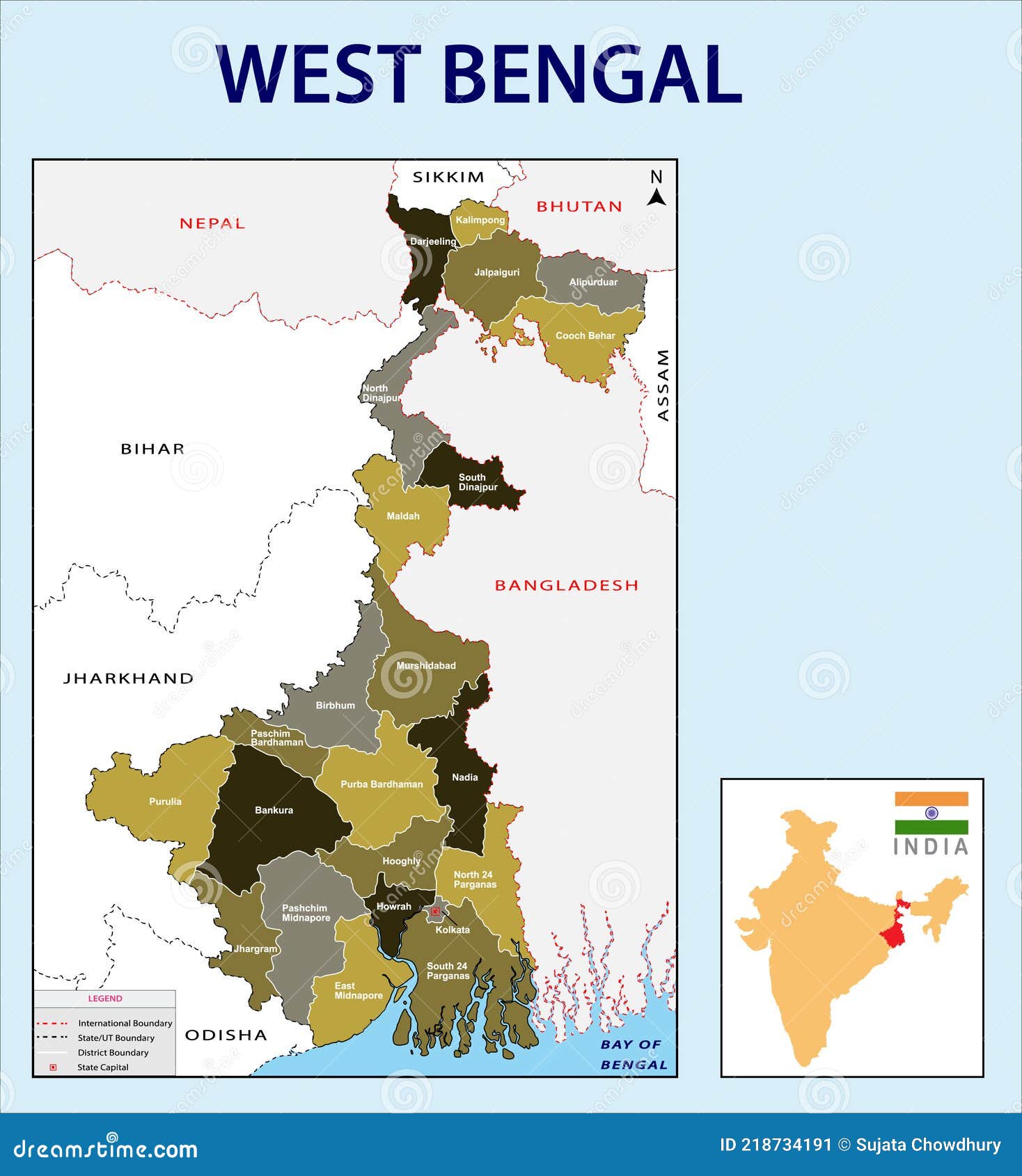
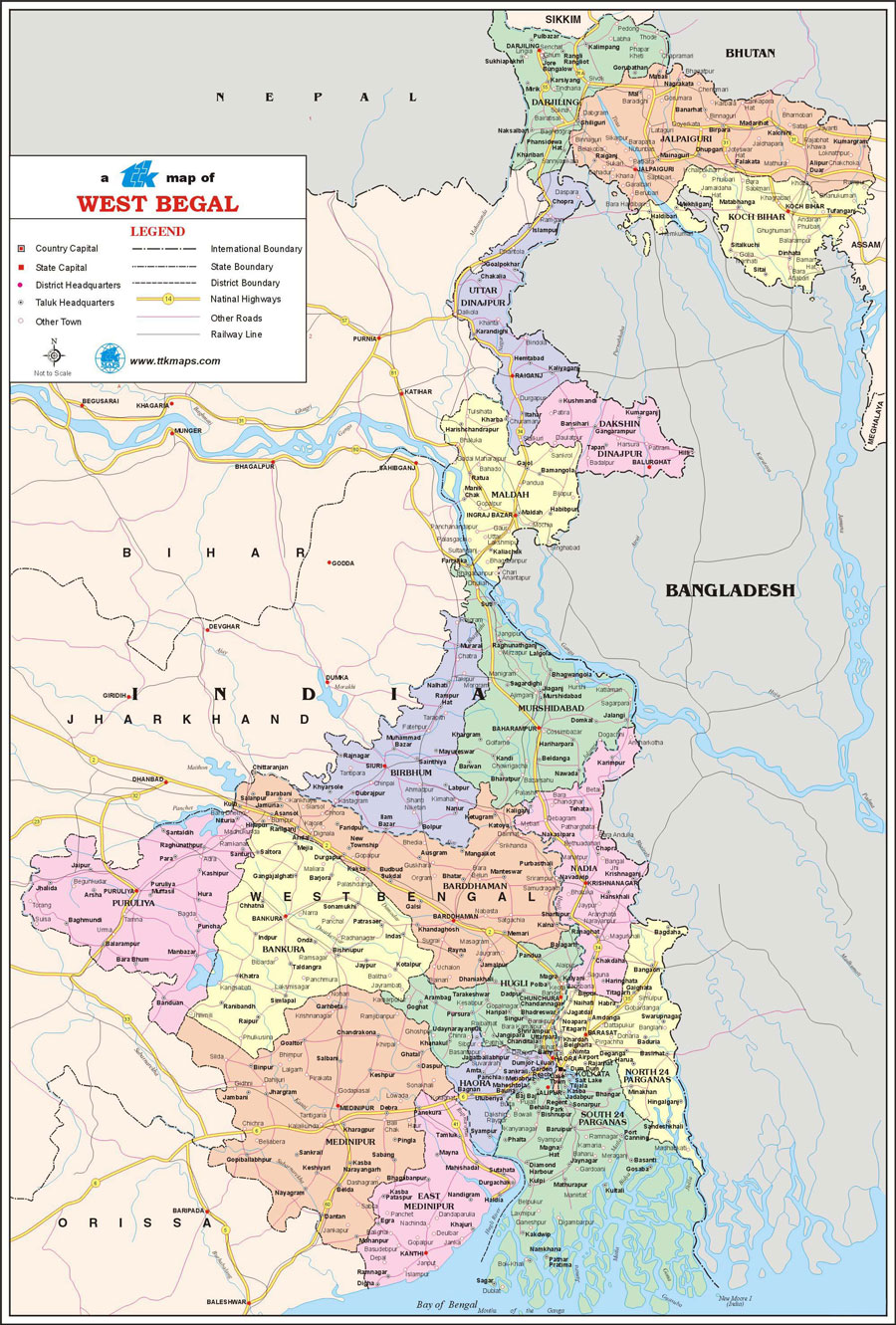
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping West Bengal: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Geographic Tapestry. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!