Navigating The North: A Comprehensive Look At The Alaska-Canada Border
By admin / May 25, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Navigating the North: A Comprehensive Look at the Alaska-Canada Border
Related Articles: Navigating the North: A Comprehensive Look at the Alaska-Canada Border
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the North: A Comprehensive Look at the Alaska-Canada Border. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the North: A Comprehensive Look at the Alaska-Canada Border
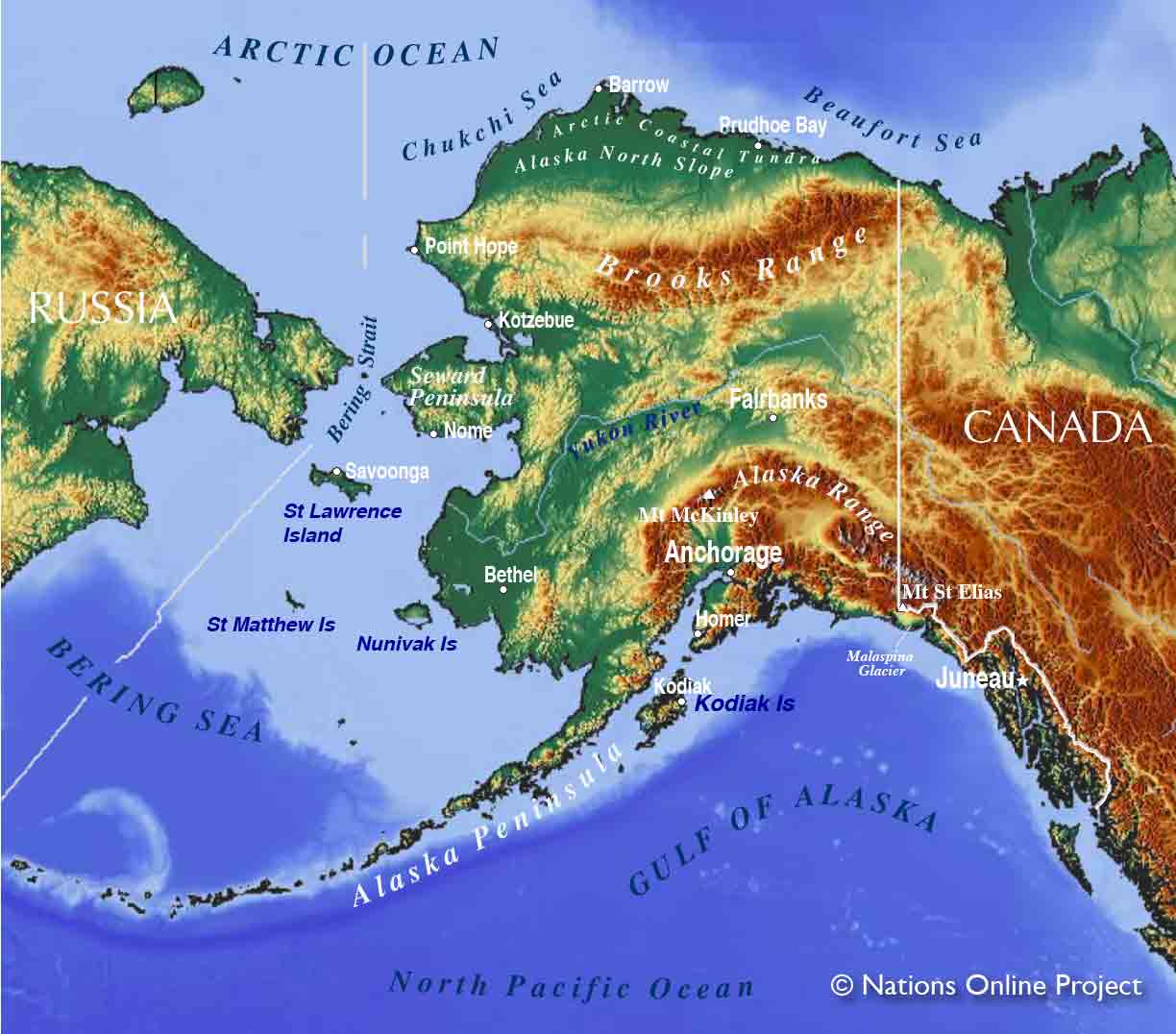
The border between Alaska and Canada, a unique geographical feature, represents a complex tapestry of history, geography, and cultural exchange. It is not simply a line on a map but a living boundary that shapes the lives of people, wildlife, and the very environment it traverses. This article delves into the intricacies of the Alaska-Canada border, exploring its historical origins, geographical significance, and contemporary relevance.
A History of Borders and Boundaries
The Alaska-Canada border, spanning over 2,000 miles, is a product of historical agreements and political negotiations. The initial establishment of the border dates back to the late 18th and early 19th centuries, a period marked by European exploration and territorial claims in North America.
- The Russian Era: Russia, having established a presence in Alaska in the 18th century, claimed the land as part of its vast empire. The southern boundary of this Russian territory extended southward along the 141st meridian west, a line that would later form the basis of the Alaska-Canada border.
- The British Claim: Meanwhile, British exploration and colonization in the region led to claims on lands further south, including what is now British Columbia. The 141st meridian, therefore, became the dividing line between Russian and British territories.
- The Purchase of Alaska: In 1867, the United States purchased Alaska from Russia. This transfer of ownership solidified the 141st meridian as the official border between Alaska (now a US territory) and British Columbia (part of Canada).
A Geographical Tapestry
The Alaska-Canada border is not a straight line but follows a complex path dictated by natural features. It traverses diverse landscapes, including:
- The Coastline: Along the Pacific coast, the border follows the intricate coastline, including numerous islands and inlets. This section of the border is characterized by mountainous terrain, dense forests, and rich marine ecosystems.
- The Mountain Ranges: The border climbs through the towering peaks of the Coast Mountains, the St. Elias Mountains, and the Brooks Range. These rugged mountains are home to glaciers, rivers, and a vast wilderness.
- The Yukon River: The Yukon River, a major waterway, forms a significant portion of the border. Its course meanders through the interior of Alaska and Canada, connecting various communities and providing access to remote regions.
Beyond the Line: Cultural Exchange and Shared Resources
The Alaska-Canada border is not just a physical boundary but also a conduit for cultural exchange and resource sharing.
- Indigenous Peoples: The border has been inhabited for millennia by indigenous peoples, including the Tlingit, Haida, and Tsimshian in Alaska and the First Nations in Canada. These communities have long-standing relationships with each other, maintaining cultural connections and shared traditions.
- Economic Ties: The border region fosters economic ties between Alaska and Canada. Trade, tourism, and resource extraction are important activities that connect communities on both sides. For example, the Alaska Highway, a vital transportation route, connects Alaska to the Canadian road network, facilitating trade and travel.
- Environmental Cooperation: The shared environment of the border region necessitates close cooperation on environmental issues. Transboundary rivers, wildlife migration patterns, and climate change require joint efforts to manage and protect the natural resources.
Challenges and Opportunities
The Alaska-Canada border presents unique challenges and opportunities for both countries.
- Border Security: With increasing concerns about terrorism and illegal immigration, border security is a priority for both countries. The remote nature of the border and the vast wilderness present challenges for enforcement agencies.
- Resource Management: The border region is rich in natural resources, including oil, gas, minerals, and timber. The exploitation of these resources requires careful planning and cooperation to ensure sustainable development and environmental protection.
- Climate Change: The impacts of climate change are particularly evident in the Arctic region, including Alaska and Canada. Melting glaciers, rising sea levels, and shifting ecosystems require collaborative efforts to mitigate climate change and adapt to its consequences.
FAQs about the Alaska-Canada Border
1. Why is the Alaska-Canada border so long and complex?
The Alaska-Canada border is long and complex due to the historical claims and negotiations that led to its establishment. It follows natural features like coastlines and mountain ranges, creating a winding and geographically diverse boundary.
2. What are the main challenges faced by both countries in managing the border?
Managing the Alaska-Canada border presents challenges in border security, resource management, and climate change adaptation. The remote and vast wilderness of the region requires sophisticated strategies for monitoring and enforcement.
3. How does the border impact the indigenous communities living in the region?
The border has historically impacted indigenous communities by dividing traditional territories and creating barriers to cultural exchange. However, there are ongoing efforts to recognize and respect indigenous rights and promote cross-border cooperation.
4. What are the economic implications of the border for both countries?
The Alaska-Canada border facilitates trade, tourism, and resource extraction, creating economic opportunities for both countries. However, economic development must be balanced with environmental protection and the interests of local communities.
5. What are the future prospects for the Alaska-Canada border?
The Alaska-Canada border will continue to be a dynamic and evolving boundary. Future challenges will include addressing climate change, managing shared resources, and promoting cross-border cooperation on issues of mutual interest.
Tips for Visiting the Alaska-Canada Border
- Plan Your Trip: The border region is vast and remote, so proper planning is essential. Research transportation options, lodging, and attractions in advance.
- Respect the Environment: The wilderness of the border region is fragile and needs to be protected. Leave no trace and follow all rules and regulations.
- Learn About the History and Culture: The border region is rich in history and culture. Take the opportunity to learn about the indigenous peoples, the fur trade, and the gold rush.
- Be Prepared for Weather Extremes: The weather in the border region can be unpredictable, with extreme temperatures and precipitation. Dress in layers and be prepared for all conditions.
- Consider a Guided Tour: Guided tours can enhance your experience by providing insights into the local history, culture, and environment.
Conclusion
The Alaska-Canada border is a testament to the complex interplay of history, geography, and human interaction. It represents a shared heritage, a dynamic landscape, and a constant reminder of the interconnectedness of the North American continent. Understanding the intricacies of this border is crucial for fostering cooperation, managing resources, and navigating the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.



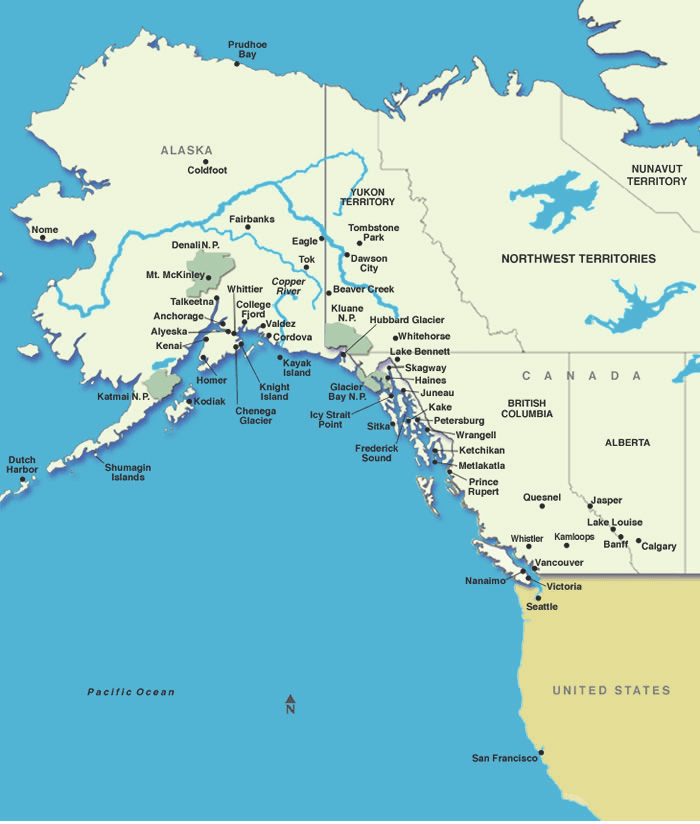



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the North: A Comprehensive Look at the Alaska-Canada Border. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!