Navigating The Tracks: A Comprehensive Look At Scotland’s Railway Network
By admin / June 28, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Navigating the Tracks: A Comprehensive Look at Scotland’s Railway Network
Related Articles: Navigating the Tracks: A Comprehensive Look at Scotland’s Railway Network
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Tracks: A Comprehensive Look at Scotland’s Railway Network. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Tracks: A Comprehensive Look at Scotland’s Railway Network
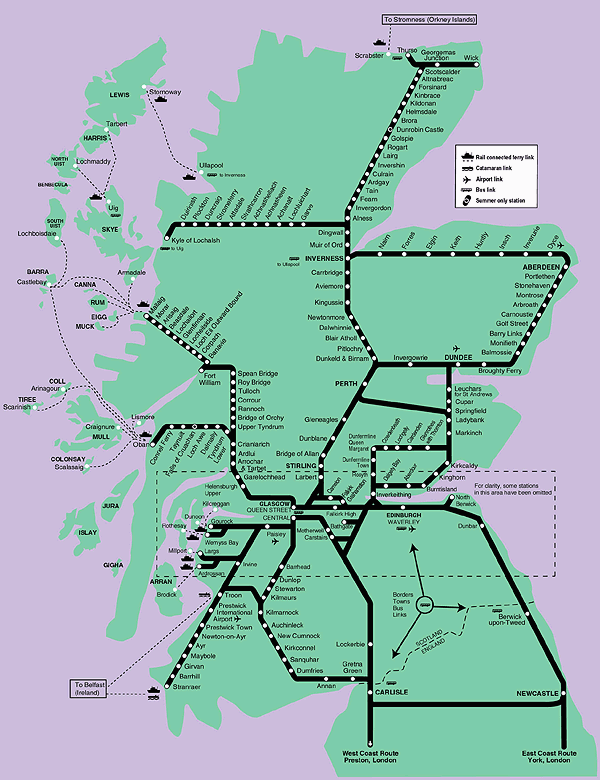
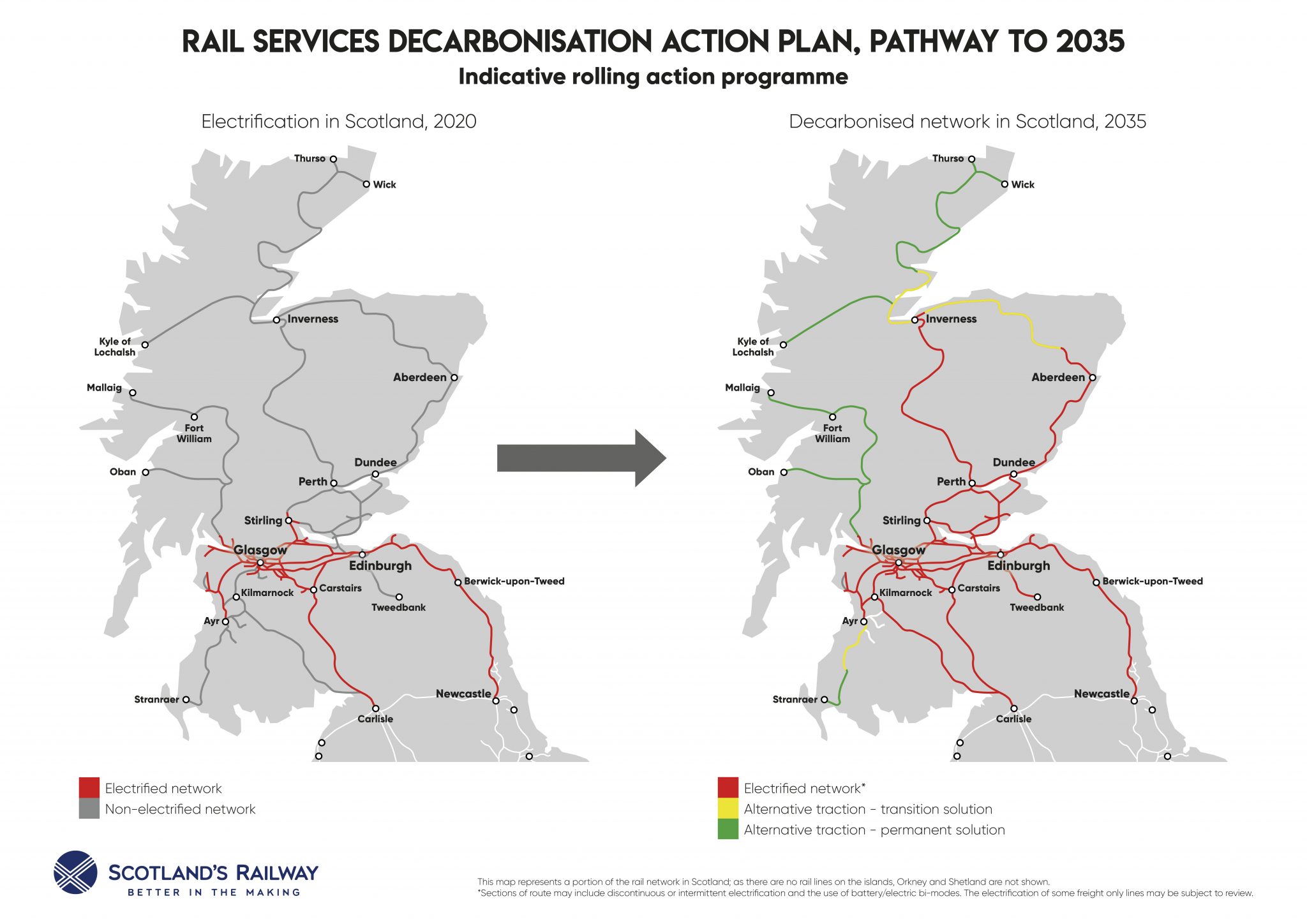
Scotland’s railway network, a sprawling web of steel and concrete, plays a vital role in the country’s economic, social, and cultural fabric. From bustling city lines to scenic coastal routes, this intricate system connects communities, facilitates trade, and provides a crucial link to the wider world. Understanding the structure and history of this network offers insights into the nation’s development and its future aspirations.
A Historical Journey: From Steam to Modernity
Scotland’s railway story began in the 19th century, a period marked by industrial expansion and a burgeoning need for efficient transportation. The first railway line, connecting Edinburgh and Dalkeith, opened in 1831, igniting a wave of construction across the country. This early period saw the emergence of numerous independent railway companies, each with its own distinct network and operating practices.
The late 19th century witnessed the consolidation of these independent companies into larger entities, culminating in the creation of the "Big Four" – the Caledonian Railway, the North British Railway, the Highland Railway, and the Great North of Scotland Railway. This consolidation brought about a degree of standardization and efficiency, but also led to a complex patchwork of lines, each with its own gauge and signaling system.
The 20th century saw further changes, including the nationalization of the railways in 1948, which led to the formation of British Railways. This period saw significant investment in infrastructure, including the electrification of certain lines and the introduction of diesel locomotives. However, the latter half of the century was marked by a decline in passenger numbers and a gradual shift towards road transport.
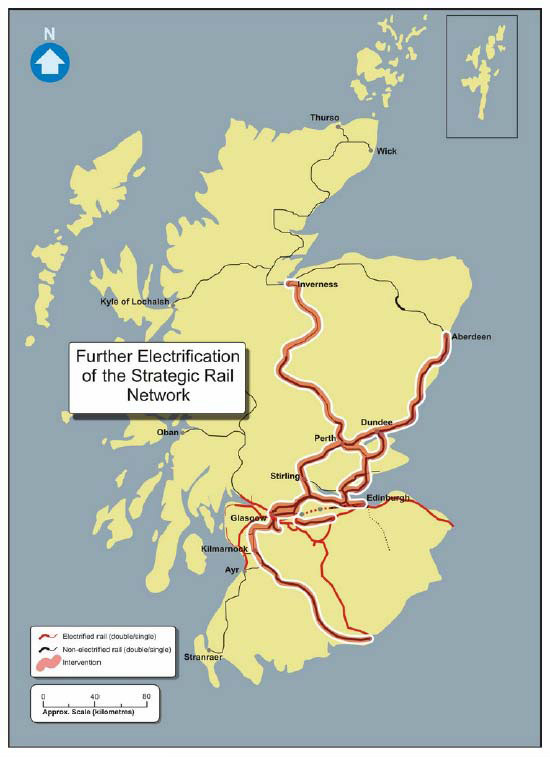
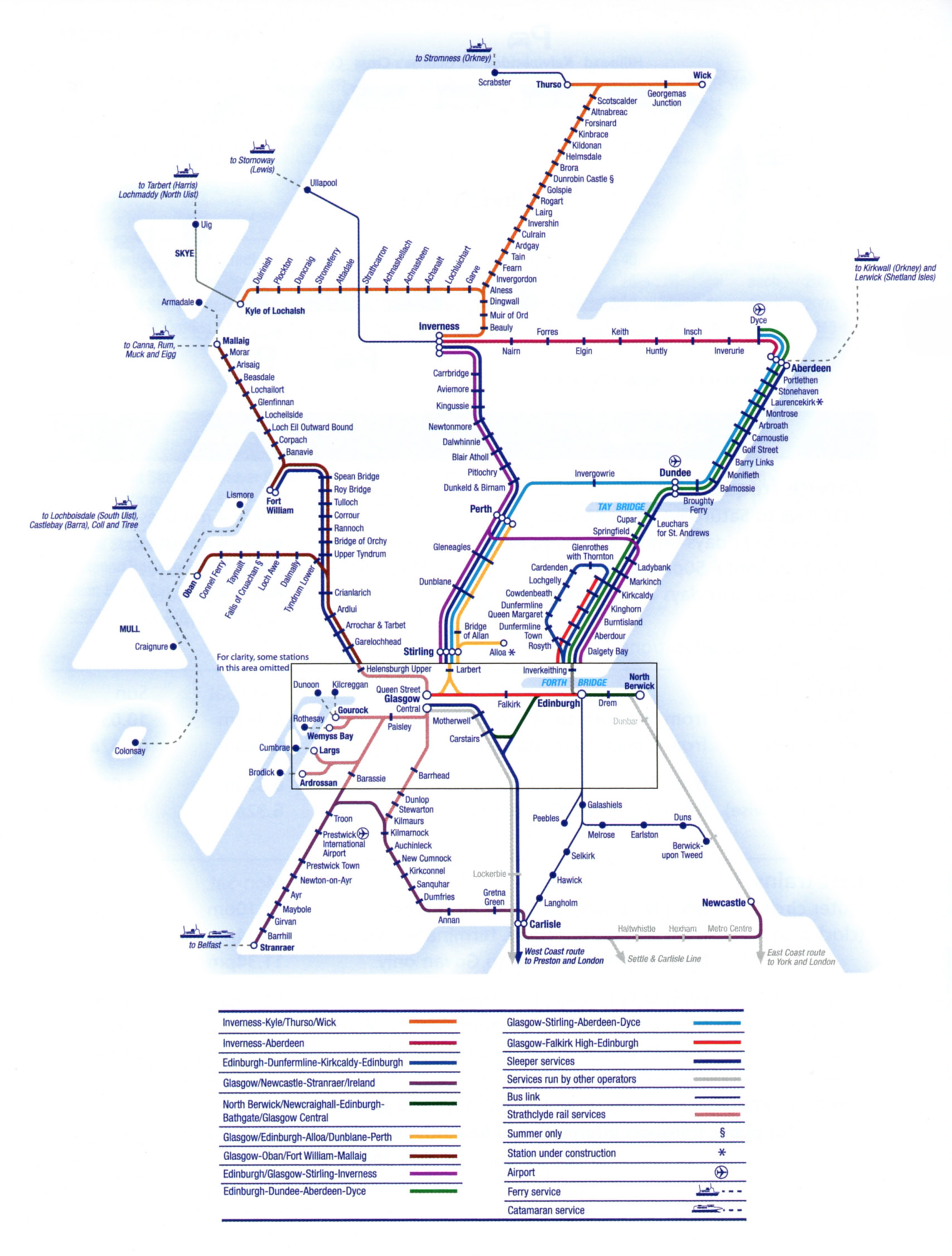
The Modern Network: A Complex Tapestry
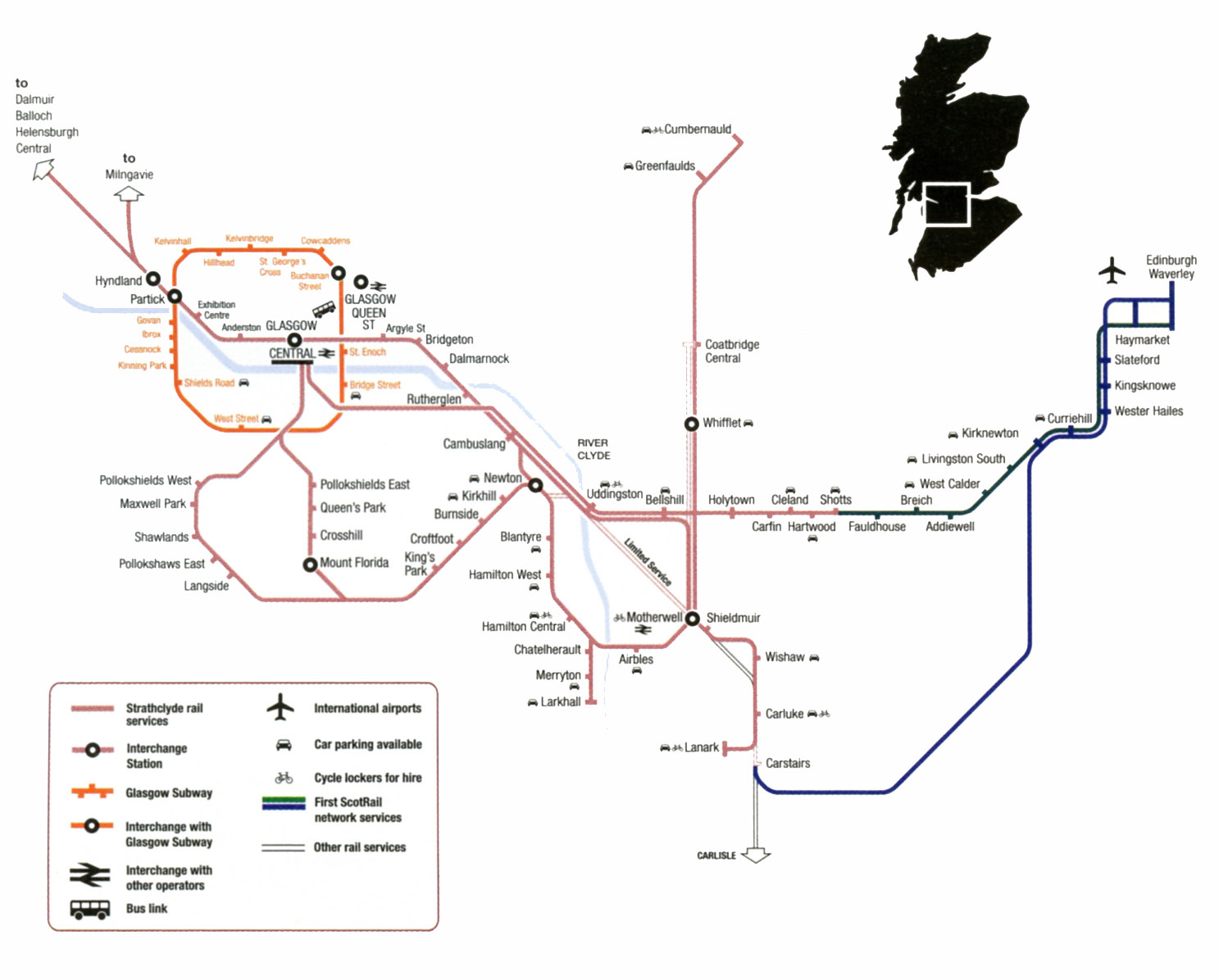
Today, Scotland’s railway network is managed by ScotRail, a subsidiary of Abellio, under a franchise agreement with the Scottish Government. The network comprises over 2,200 miles of track, connecting major cities, towns, and rural communities across the country.
Key Components of the Network:
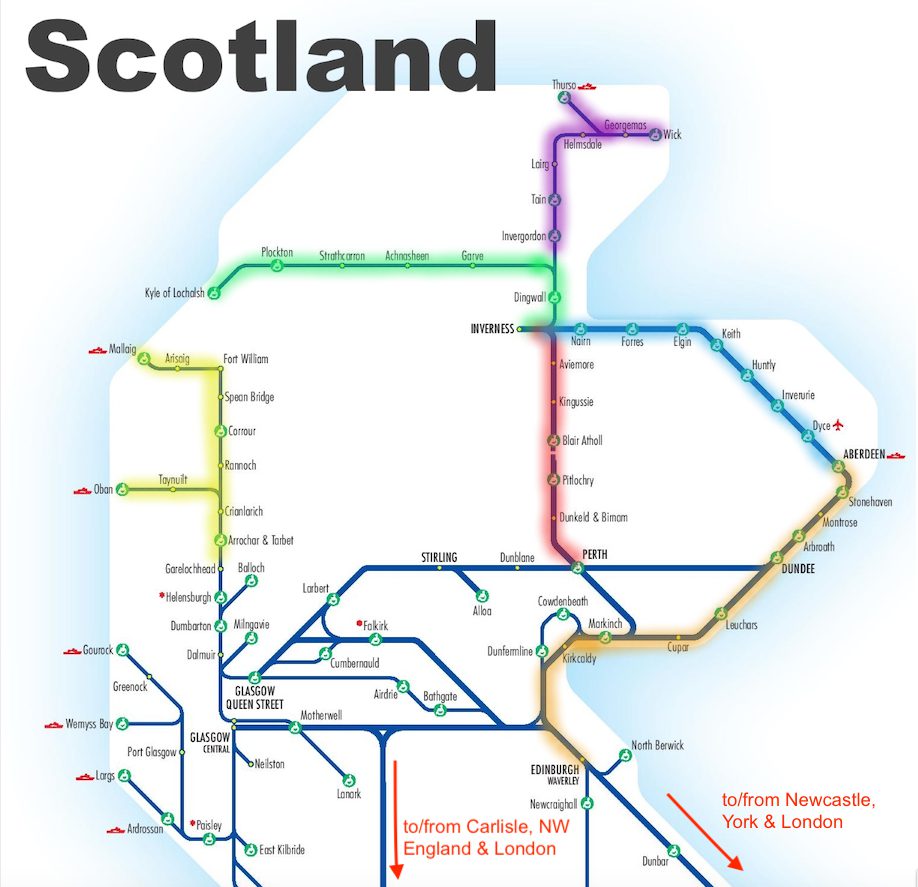
- The West Coast Main Line: This high-speed route, running from London to Glasgow, forms the backbone of the Scottish network. It carries significant passenger and freight traffic and is vital for connecting Scotland to the rest of the UK.
- The East Coast Main Line: This route runs from London to Edinburgh and is another major artery for passenger and freight traffic. It provides a vital link to the major cities of the east coast of Scotland.
- Cross-Country Routes: Numerous cross-country routes connect major cities and towns, providing vital links for regional travel. These routes include the Highland Main Line, which runs from Edinburgh to Inverness, and the Aberdeen-Inverness line, which traverses the north-east of Scotland.
- Branch Lines: A network of branch lines extend from the main lines, connecting smaller towns and villages to the wider network. These lines play a vital role in supporting local economies and providing essential transport links for rural communities.
Challenges and Opportunities
Scotland’s railway network faces numerous challenges, including:
- Infrastructure Investment: The network requires significant investment to maintain existing infrastructure and to improve capacity and efficiency.
- Competition from Road Transport: The rise of road transport continues to pose a challenge to the rail sector, particularly for passenger traffic.
- Decentralization: The Scottish Government’s commitment to decentralization presents both opportunities and challenges for the rail network.
Benefits of a Well-Functioning Railway Network:
- Economic Growth: A well-functioning railway network supports economic growth by facilitating trade, connecting businesses, and attracting investment.
- Social Inclusion: Railways provide vital links to communities, enabling access to employment, education, and healthcare.
- Environmental Sustainability: Rail transport offers a sustainable alternative to road transport, reducing carbon emissions and congestion.
FAQs
- What is the fastest train in Scotland? The fastest train in Scotland is the InterCity 225, capable of reaching speeds of 125 miles per hour.
- What is the longest railway line in Scotland? The longest railway line in Scotland is the Highland Main Line, stretching for over 200 miles from Edinburgh to Inverness.
- Are there any underground railways in Scotland? Scotland does not have any underground railways, although Glasgow and Edinburgh have extensive tram networks.
- What are the main types of trains used in Scotland? The main types of trains used in Scotland include InterCity 225, Class 156, and Class 170.
Tips for Using Scotland’s Railway Network:
- Plan your journey in advance: Check train times and fares online or using the ScotRail app.
- Purchase tickets in advance: Booking tickets online or at a station can often save money.
- Be aware of peak times: Train services can be busier during peak hours, so allow extra time for travel.
- Check for disruptions: Keep up-to-date with any planned engineering works or disruptions by checking ScotRail’s website or app.
Conclusion
Scotland’s railway network is a vital asset for the country, connecting communities, facilitating trade, and supporting economic growth. While facing challenges, the network continues to evolve and adapt to the changing needs of the nation. With continued investment and innovation, Scotland’s railways are poised to play an even greater role in shaping the country’s future.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Tracks: A Comprehensive Look at Scotland’s Railway Network. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!