South America: A Continent Straddling The Equator
By admin / April 23, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
South America: A Continent Straddling the Equator
Related Articles: South America: A Continent Straddling the Equator
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to South America: A Continent Straddling the Equator. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
South America: A Continent Straddling the Equator
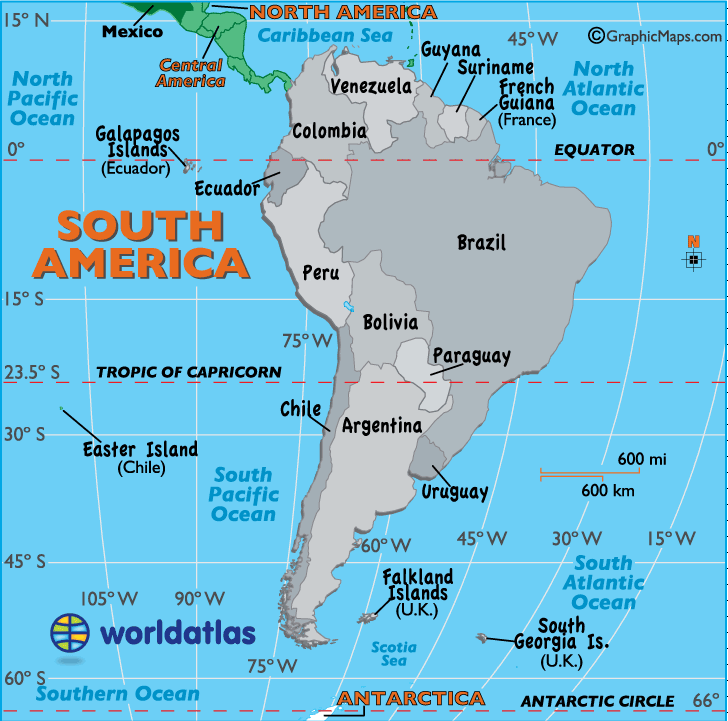
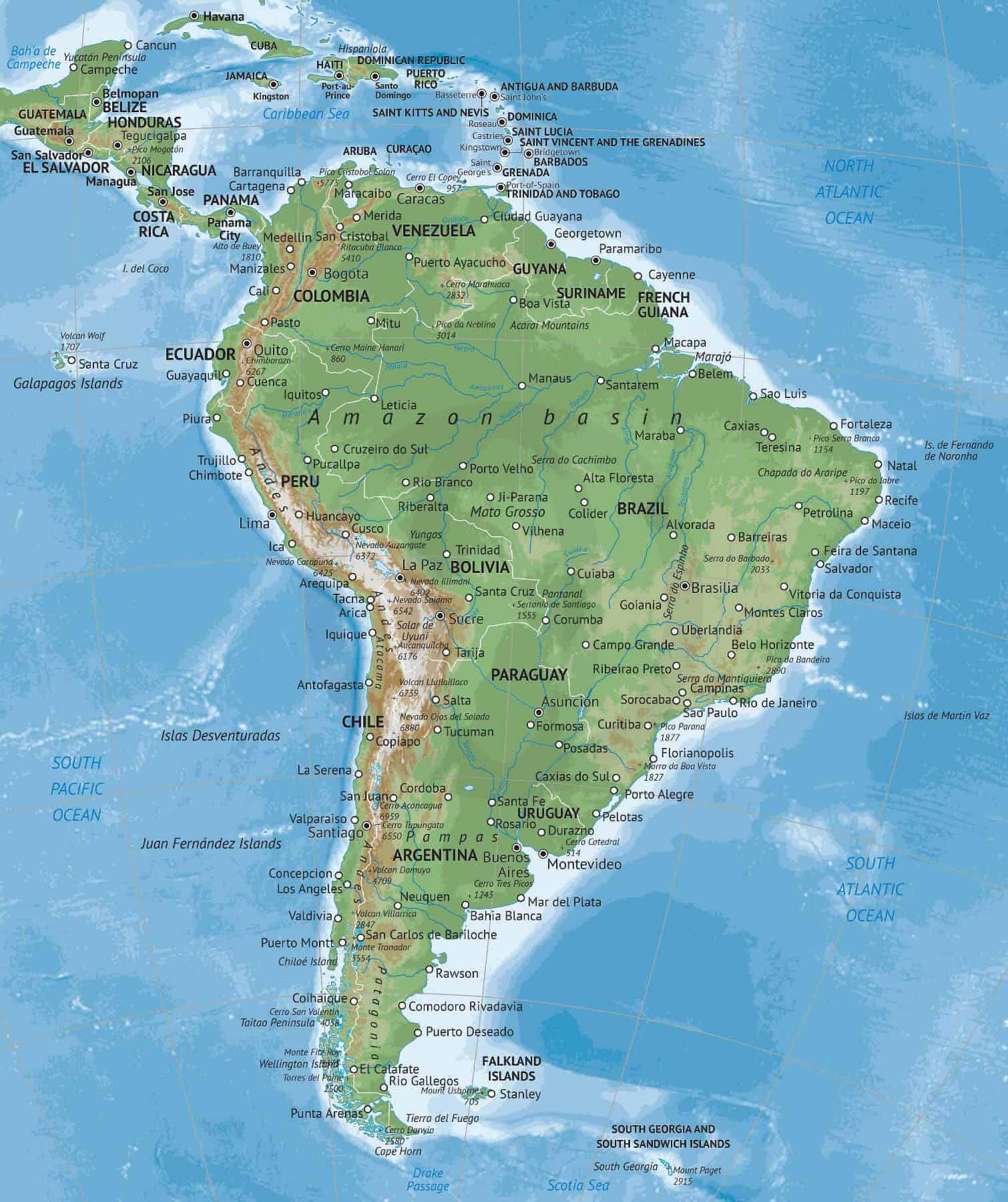
South America, the fourth-largest continent, is geographically unique for its position straddling the equator. This geographical feature significantly influences its climate, biodiversity, and cultural landscape. Understanding the relationship between South America and the equator allows for a deeper appreciation of its diverse ecosystems, vibrant cultures, and historical development.
The Equator’s Influence on South America’s Climate
The equator acts as a dividing line, separating the northern and southern hemispheres. Its location directly impacts the distribution of solar radiation, influencing the climate of South America. The region lying directly on the equator experiences a tropical climate characterized by consistent high temperatures, abundant rainfall, and high humidity. This equatorial climate fosters the growth of lush rainforests, such as the Amazon Rainforest, a vital carbon sink and a biodiversity hotspot.
Moving away from the equator, the climate gradually transitions. The northern and southern regions experience distinct seasons, with varying levels of rainfall and temperature fluctuations. Coastal areas are generally influenced by ocean currents, leading to more moderate temperatures and a higher degree of precipitation. The Andes Mountains, running along the western edge of the continent, create a rain shadow effect, resulting in drier climates on the eastern side.
Biodiversity and Ecosystems Shaped by the Equator
The equator’s influence on South America’s climate is directly reflected in its diverse ecosystems. The Amazon rainforest, home to an estimated 10% of the world’s known species, thrives in the equatorial region. This vast ecosystem supports a complex web of life, including countless species of plants, animals, insects, and microorganisms.
Other equatorial ecosystems include the Andean cloud forests, characterized by high humidity and endemic species. These forests are crucial for water regulation and provide a habitat for numerous endangered species. The vast savannas of the Cerrado biome, found primarily in Brazil, are also influenced by the equatorial climate, showcasing unique plant and animal adaptations to the dry season.
Cultural and Historical Significance
The equator’s influence extends beyond the physical environment, shaping the cultural and historical development of South America. Indigenous communities have long inhabited the equatorial regions, developing unique traditions and knowledge systems adapted to their environment. The Amazon rainforest, for instance, holds significant cultural importance for indigenous communities, providing sustenance, medicinal resources, and spiritual connection.
Equatorial regions have also played a crucial role in the development of South America’s colonial history. The abundance of natural resources, particularly in the equatorial rainforest, attracted European powers seeking to exploit the region’s wealth. This historical context continues to shape the socio-economic landscape of South America, with equatorial regions often experiencing challenges related to resource extraction, deforestation, and social inequality.
Exploring South America’s Equatorial Regions
Traveling through South America’s equatorial regions provides a unique opportunity to experience the continent’s diverse ecosystems and cultures. The Amazon rainforest offers an unforgettable adventure, with opportunities for wildlife viewing, exploring indigenous communities, and gaining a deeper understanding of the rainforest’s ecological significance.
Other equatorial destinations include the Galapagos Islands, known for their unique flora and fauna, and the Amazonian city of Manaus, a gateway to the rainforest and a vibrant cultural hub.
Understanding South America’s Equatorial Significance
Understanding the influence of the equator on South America is crucial for appreciating the continent’s diverse natural resources, cultural heritage, and historical development. The equator’s impact on climate, biodiversity, and cultural landscapes highlights the interconnectedness of the natural world and human societies.
By exploring the equatorial regions of South America, travelers and researchers can gain a deeper understanding of the continent’s unique characteristics and the importance of conservation and sustainable development in preserving its diverse ecosystems and cultural heritage.
FAQs
Q: What are the main characteristics of South America’s equatorial climate?
A: The equatorial climate in South America is characterized by consistently high temperatures, abundant rainfall, and high humidity. It is typically hot and humid year-round, with little variation in temperature.
Q: How does the equator influence the biodiversity of South America?
A: The equator’s influence on climate, particularly its consistent warm temperatures and high rainfall, fosters the growth of diverse ecosystems, such as the Amazon rainforest, which is home to a significant portion of the world’s biodiversity.
Q: What are some of the cultural impacts of the equator on South America?
A: The equator has shaped indigenous cultures in South America, influencing their traditional knowledge systems, subsistence practices, and spiritual beliefs. It has also played a role in the development of colonial history and the current socio-economic landscape.
Q: What are some of the environmental challenges facing South America’s equatorial regions?
A: Environmental challenges in South America’s equatorial regions include deforestation, habitat loss, climate change, and resource extraction, all of which threaten the biodiversity and cultural heritage of these regions.
Tips
- Plan your trip to South America’s equatorial regions during the dry season to avoid heavy rainfall and humidity.
- Respect local customs and traditions when visiting indigenous communities.
- Support sustainable tourism initiatives that promote conservation and local development.
- Learn about the environmental challenges facing South America’s equatorial regions and how you can contribute to their protection.
Conclusion
The equator’s influence on South America extends far beyond its geographical location. It shapes the continent’s climate, biodiversity, cultural landscape, and historical development. By understanding the impact of the equator on South America, we can appreciate its unique characteristics and recognize the importance of preserving its diverse ecosystems and cultural heritage for future generations.
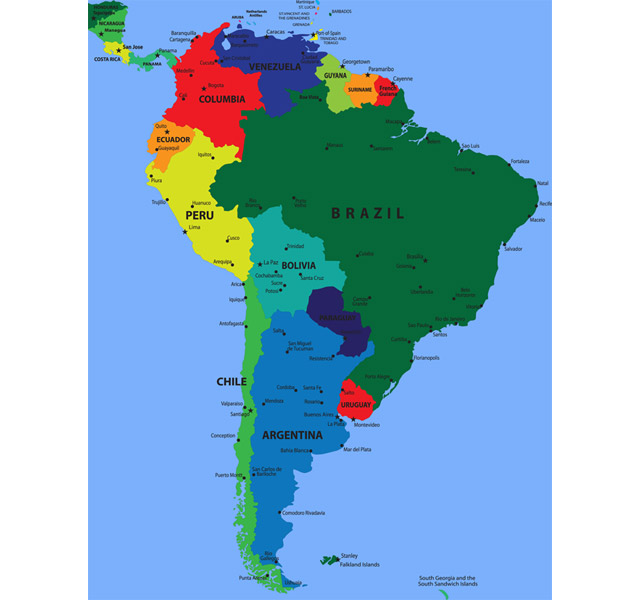



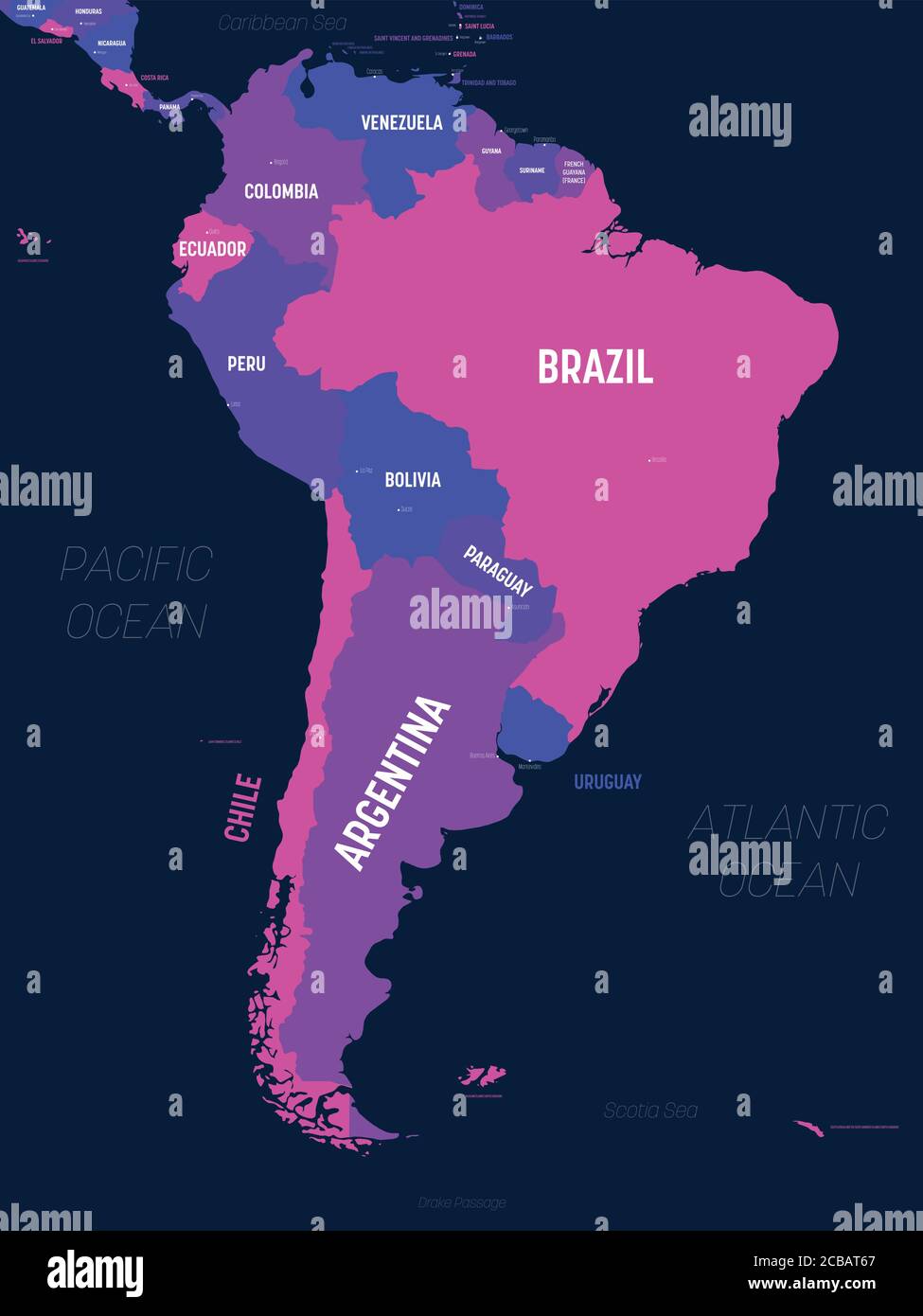
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/countries-that-lie-on-the-equator-1435319_V2-01-28e48f27870147d3a00edc1505f55770.png)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into South America: A Continent Straddling the Equator. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!