The Divided Landscape: Understanding The Geographic Distribution Of American Political Parties
By admin / March 22, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
The Divided Landscape: Understanding the Geographic Distribution of American Political Parties
Related Articles: The Divided Landscape: Understanding the Geographic Distribution of American Political Parties
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Divided Landscape: Understanding the Geographic Distribution of American Political Parties. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Divided Landscape: Understanding the Geographic Distribution of American Political Parties
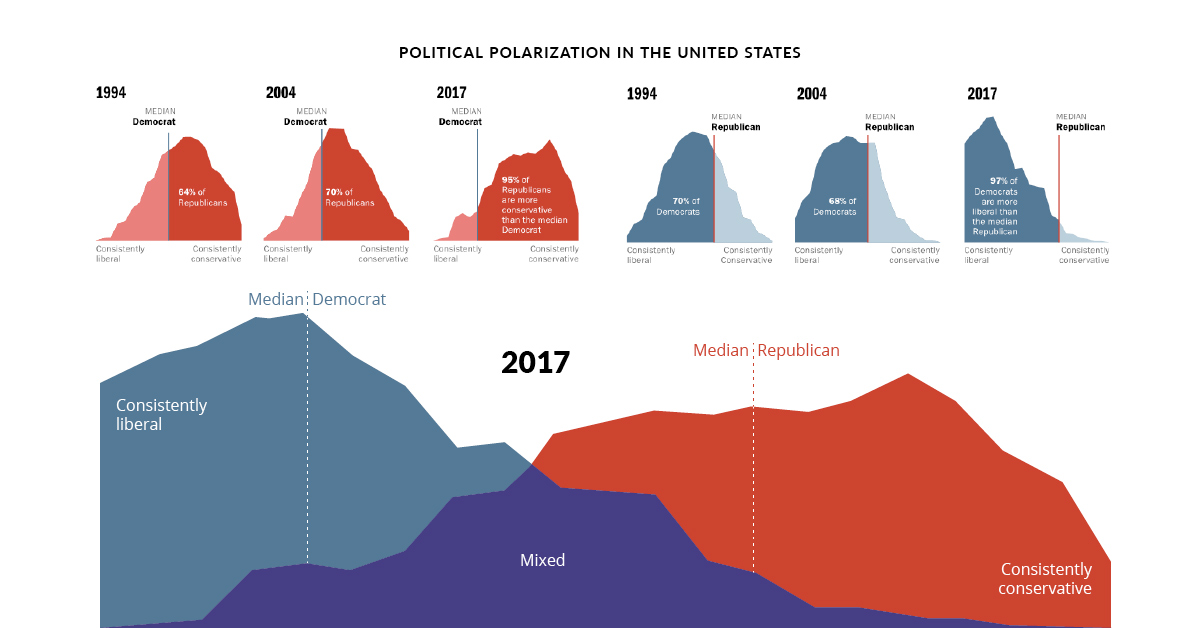
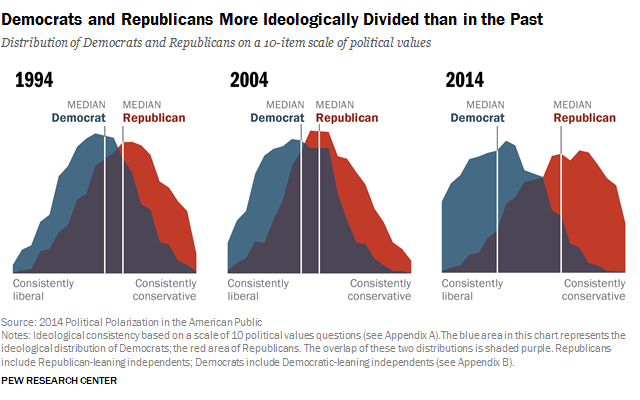
The United States, a nation founded on the principle of "We the People," is often portrayed as a melting pot of diverse ideologies. This diversity manifests itself in the political landscape, with two major parties – the Democrats and Republicans – dominating the national discourse. While the ideological divide between these parties is widely discussed, their geographic distribution across the country offers a unique lens to understand the complex interplay of political affiliation, demographics, and social values.
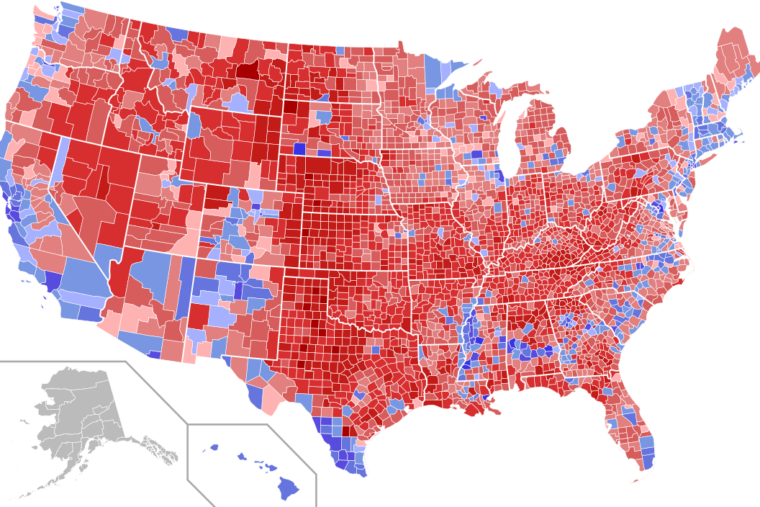
Mapping the Red and Blue:
Visualizing the distribution of Democrats and Republicans on a map provides a powerful tool for understanding political trends. The traditional "red state" versus "blue state" dichotomy, where red represents Republican strongholds and blue signifies Democrat-leaning areas, offers a simplistic but effective initial understanding.
However, this binary approach can be misleading. Examining the map at a more granular level reveals a complex mosaic of political preferences. While some states consistently lean towards one party or the other, many exhibit a significant degree of internal variation. Within states, individual counties and even smaller geographic units can display distinct political affiliations, reflecting the diverse viewpoints within a single region.
Factors Influencing the Political Landscape:
Several factors contribute to the geographic distribution of political parties in the United States:
- Demographics: Population density, racial composition, education levels, and income distribution all play a significant role. Urban areas tend to lean towards Democratic candidates, while rural areas often favor Republicans. This correlation is linked to differing perspectives on issues like social programs, economic policies, and environmental regulations.
- Historical Factors: The historical legacy of a region, including its economic development, social movements, and political figures, shapes the political landscape. States with strong labor union traditions often have a more Democratic electorate, while regions with a history of conservative values tend to lean towards Republican candidates.
- Cultural Values: Cultural and religious beliefs influence political affiliations. For instance, regions with strong evangelical Christian populations often vote Republican, while areas with a more diverse religious landscape may be more receptive to Democratic candidates.
- Economic Factors: Economic conditions and employment opportunities impact political preferences. Regions experiencing economic hardship may favor policies that address their concerns, often aligning with the Democratic party. Conversely, areas with robust economies might support Republican policies perceived as pro-business.
- Media Influence: Media coverage, including local news and social media platforms, can shape public opinion and political attitudes. Regions with access to diverse media sources may exhibit a more nuanced political landscape compared to areas with limited media options.
Beyond the Map:
While maps provide a valuable visual representation of political distribution, it’s crucial to recognize their limitations. Maps often simplify complex realities, neglecting the nuances of individual voter preferences and the dynamic nature of political affiliations.
Furthermore, the geographic distribution of political parties is not static. Shifts in demographics, economic conditions, and social values can lead to changes in political preferences over time. This fluidity is reflected in the emergence of "purple" states, where neither party holds a clear majority, indicating a growing political polarization.
FAQs Regarding the Map of Democrats and Republicans:
1. What is the significance of the "red" and "blue" color scheme?
The use of red and blue to represent Republican and Democratic strongholds, respectively, is a relatively recent phenomenon. It originated in the 1980s and became widely adopted in the 1990s. The specific choice of colors is attributed to various factors, including the use of red and blue to denote opposing political parties in earlier maps and the association of red with Republican values like strength and tradition and blue with Democratic values like progress and unity.
2. Are there any specific geographic patterns within states?
Yes, within states, there are often distinct political patterns. Urban areas tend to be more Democratic, while rural areas are often more Republican. This pattern is particularly pronounced in larger states with diverse geographic landscapes and demographics.
3. How do demographic shifts impact the map of Democrats and Republicans?
Demographic changes, such as population growth, migration, and changes in racial composition, can significantly impact the political landscape. For instance, increasing Hispanic populations in certain regions have led to a shift in political preferences, as Hispanic voters tend to lean towards Democratic candidates.
4. What are the implications of a growing number of "purple" states?
The emergence of "purple" states, where neither party holds a clear majority, suggests a growing political polarization and a decline in traditional party loyalties. This trend can lead to increased political competition and a more complex political landscape.
5. How can maps be used to understand the political landscape?
Maps provide a visual representation of political affiliations, allowing for a quick and intuitive understanding of geographic patterns. They can be used to identify regions with strong party support, areas of political competition, and demographic trends influencing political preferences.
Tips for Interpreting the Map of Democrats and Republicans:
- Consider the scale: Pay attention to the level of granularity used in the map. A map showing state-level data will provide a broader overview, while a map showing county-level data will reveal more detailed patterns.
- Look beyond the colors: While the red and blue color scheme is useful, it’s important to consider other factors contributing to political preferences. Analyze demographic data, historical context, and economic conditions to gain a deeper understanding.
- Recognize the dynamic nature of the map: Political affiliations are not static. Be aware of demographic shifts, economic changes, and social movements that can alter the political landscape over time.
- Use maps in conjunction with other data sources: Maps provide a visual representation but should be used in conjunction with other data sources, such as election results, opinion polls, and demographic statistics, to gain a comprehensive understanding of political trends.
Conclusion:
The map of Democrats and Republicans serves as a valuable tool for understanding the geographic distribution of political parties in the United States. While the traditional "red state" versus "blue state" dichotomy offers a basic understanding, examining the map at a more granular level reveals a complex and nuanced political landscape. Factors such as demographics, historical factors, cultural values, economic conditions, and media influence all contribute to the geographic patterns observed. By analyzing the map in conjunction with other data sources and recognizing its limitations, we can gain a deeper understanding of the political dynamics shaping the American nation.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Divided Landscape: Understanding the Geographic Distribution of American Political Parties. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!