Understanding The Power Of Line 3 Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
By admin / May 5, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Understanding the Power of Line 3 Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding the Power of Line 3 Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Power of Line 3 Maps: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Power of Line 3 Maps: A Comprehensive Guide

Line 3 maps are not simply visual representations of lines; they are powerful tools used in various fields, each with its own unique purpose and application. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of line 3 maps, exploring their diverse applications, significance, and benefits.
The Essence of Line 3 Maps
At its core, a line 3 map is a visual representation of data, where each line corresponds to a specific entity or attribute. The third dimension in this context refers to the line’s thickness, color, or other visual characteristics, which convey additional information about the entity it represents. This additional dimension allows for a richer understanding of the data than a simple line chart or graph.
Applications of Line 3 Maps
The versatility of line 3 maps makes them applicable across a wide range of disciplines, including:
- Data Visualization: In data analysis, line 3 maps are used to visualize complex datasets, highlighting trends, patterns, and outliers. For instance, a line 3 map could represent the number of sales transactions per month, with line thickness indicating the total value of transactions.
- Network Analysis: Line 3 maps are instrumental in visualizing and analyzing networks, such as transportation systems, communication networks, or social networks. The thickness of each line could represent the volume of traffic, bandwidth, or strength of connections.
- Spatial Analysis: In geography and spatial analysis, line 3 maps are used to represent spatial relationships and patterns. For example, a line 3 map could depict the flow of rivers, with line thickness representing the volume of water flow.
- Medical Imaging: Line 3 maps are used in medical imaging to visualize anatomical structures and diagnose diseases. For example, a line 3 map could represent the blood vessels in the brain, with line thickness indicating blood flow velocity.
- Financial Modeling: Line 3 maps can be used in financial modeling to visualize financial data, such as stock prices, interest rates, and economic indicators. Line thickness could represent the magnitude of change or volatility.
Benefits of Line 3 Maps
Line 3 maps offer several advantages over traditional line charts and graphs:
- Enhanced Data Visualization: By adding the third dimension, line 3 maps provide a more comprehensive and intuitive understanding of data.
- Improved Data Interpretation: The visual representation allows for easier identification of trends, patterns, and anomalies.
- Increased Clarity and Insight: Line 3 maps effectively convey complex data relationships, leading to deeper insights.
- Enhanced Communication: They facilitate effective communication of data findings to both technical and non-technical audiences.
- Interactive Exploration: Line 3 maps can be interactive, allowing users to explore data dynamically and gain further insights.
FAQs on Line 3 Maps
Q: What are the different types of line 3 maps?
A: Line 3 maps can be categorized based on the type of data they represent and the visual characteristics used to convey the third dimension. Some common types include:
- Line thickness maps: The line thickness represents the magnitude of the data.
- Color-coded maps: Different colors are used to represent different data values.
- Gradient maps: A gradual change in color along the line represents a change in data value.
- Animated maps: The lines change dynamically over time to represent changes in data.
Q: What software can be used to create line 3 maps?
A: There are several software programs available for creating line 3 maps, including:
- Microsoft Excel: While not specifically designed for line 3 maps, Excel can be used to create basic line charts with thickness variations.
- Tableau: A powerful data visualization software that offers advanced features for creating line 3 maps.
- Power BI: Another popular data visualization tool that allows for the creation of interactive line 3 maps.
- R: A statistical programming language with extensive libraries for data visualization, including line 3 maps.
- Python: A versatile programming language with libraries like matplotlib and seaborn that support line 3 map creation.
Q: What are the limitations of line 3 maps?
A: While line 3 maps offer significant benefits, they also have some limitations:
- Complexity: Line 3 maps can be complex and difficult to interpret for non-technical audiences.
- Data Density: Too much data can lead to cluttered and confusing maps.
- Visual Distortion: The third dimension can sometimes distort the data, making it difficult to accurately interpret.
Tips for Creating Effective Line 3 Maps
- Choose the right type of line 3 map: Select the type that best suits the data and the intended audience.
- Keep it simple: Avoid overcrowding the map with too much information.
- Use clear and concise labels: Label the axes and other important elements clearly.
- Choose appropriate colors: Select colors that are visually appealing and easy to distinguish.
- Test the map: Share the map with others for feedback and ensure it is easily understandable.
Conclusion
Line 3 maps are a valuable tool for data visualization and analysis. By adding a third dimension, they provide a more comprehensive and insightful understanding of data than traditional line charts and graphs. Their versatility makes them applicable across various fields, from data analysis and network analysis to spatial analysis and medical imaging. By understanding the principles and benefits of line 3 maps, users can leverage their power to effectively communicate data and gain deeper insights.
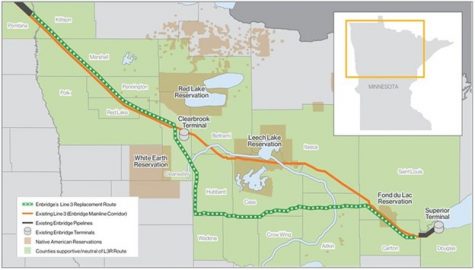
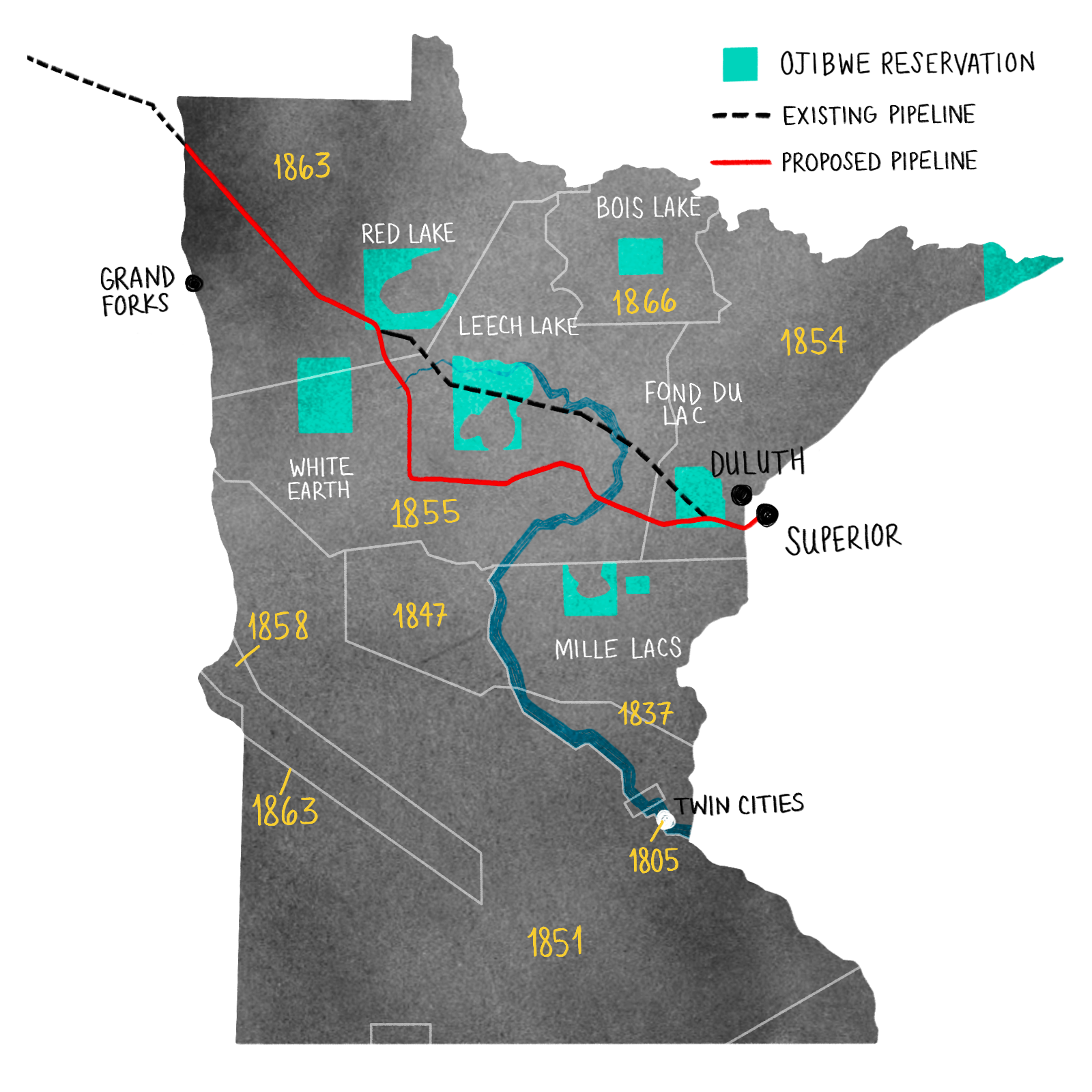

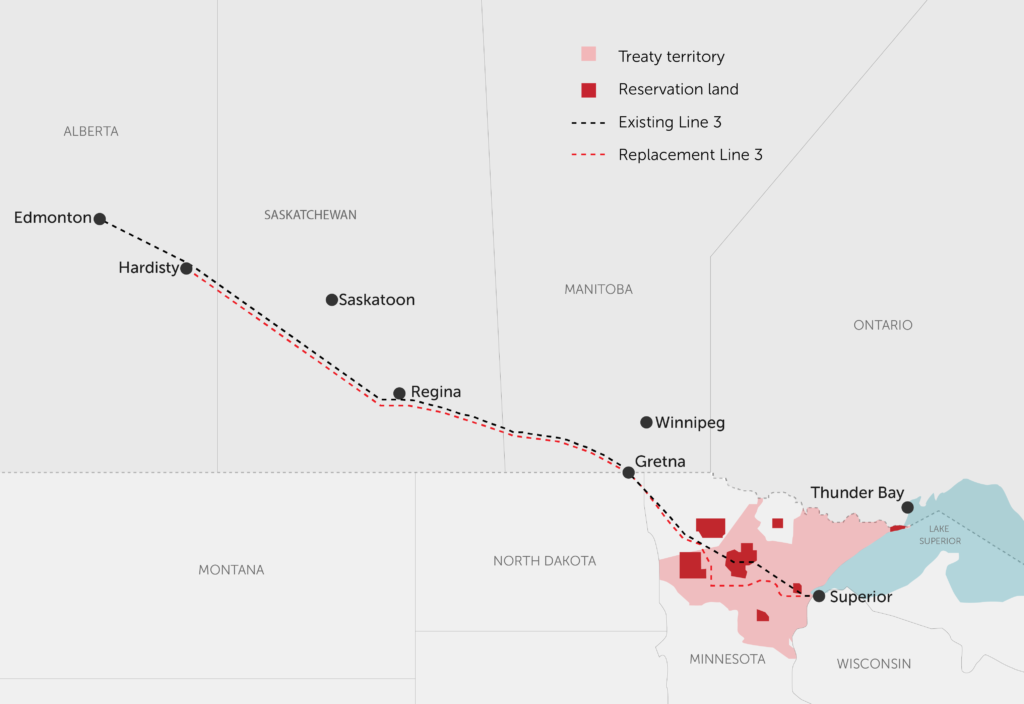

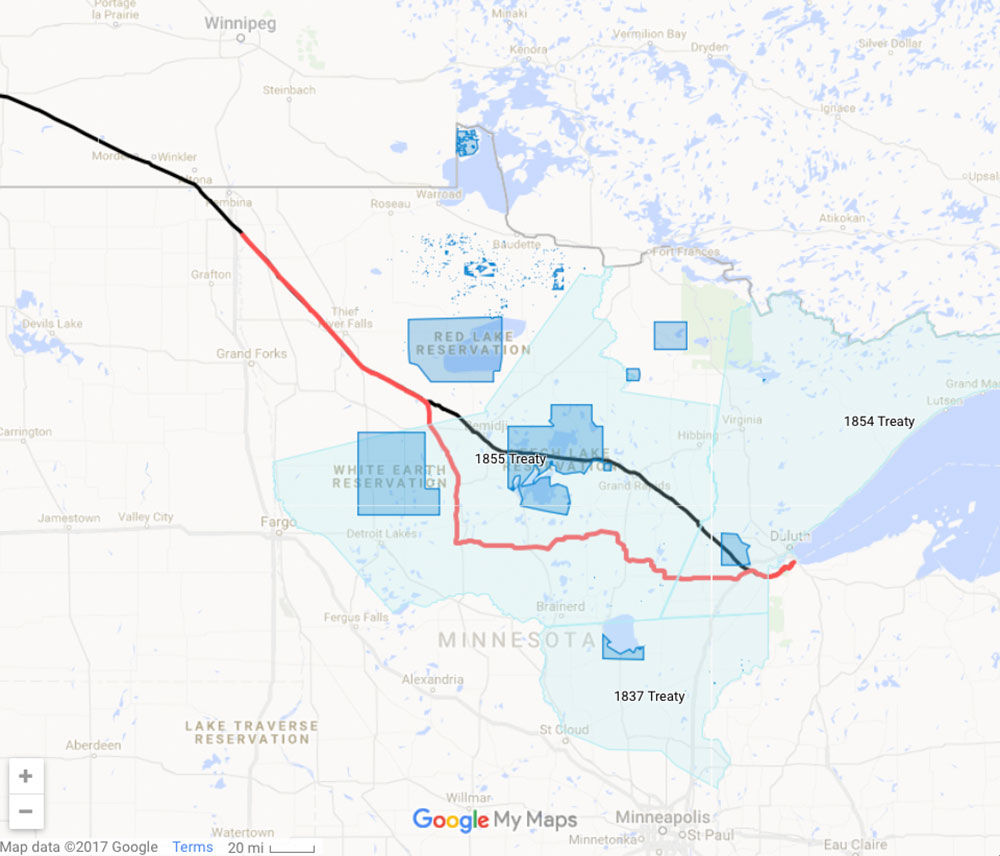


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Power of Line 3 Maps: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!