Unveiling Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide To Creating Effective Heat Maps
By admin / September 18, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Unveiling Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Creating Effective Heat Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Creating Effective Heat Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Creating Effective Heat Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Creating Effective Heat Maps
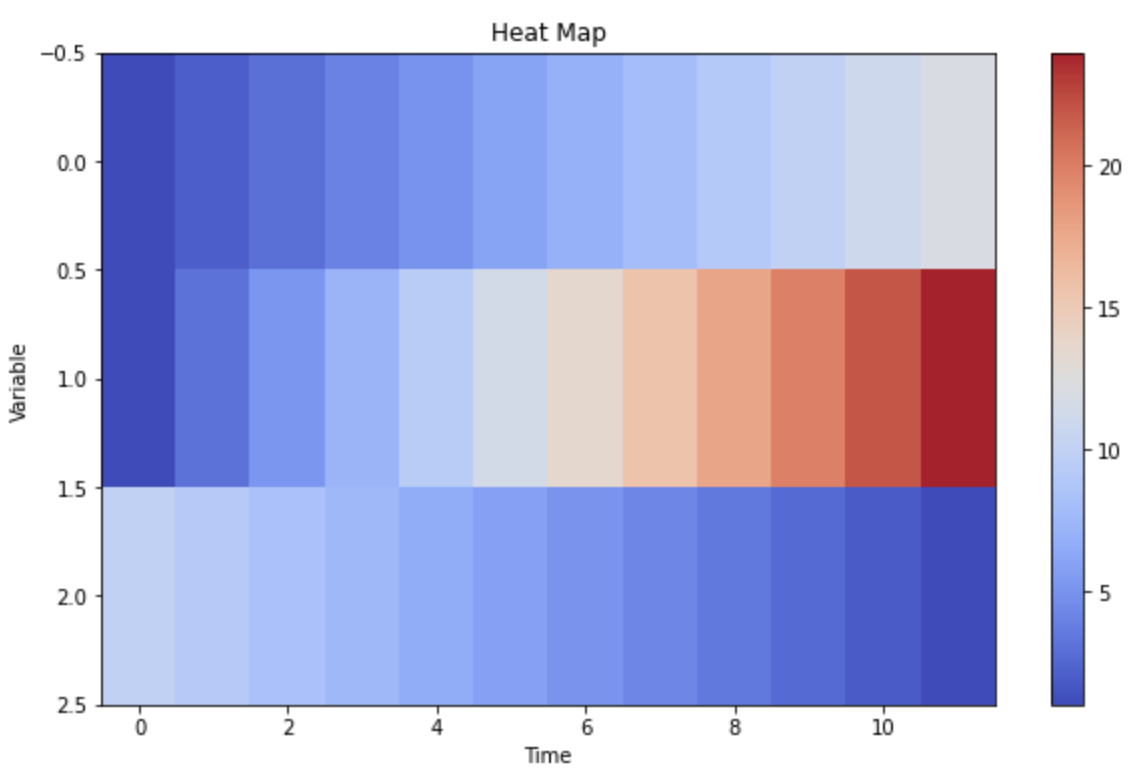
Heat maps, visual representations of data intensity, offer a powerful tool for understanding and interpreting complex datasets. They translate numerical data into a visually compelling format, enabling users to quickly identify areas of high and low activity, concentration, or significance. This article provides a comprehensive guide to creating effective heat maps, covering the fundamental concepts, diverse applications, and practical steps involved in their construction.
Understanding the Essence of Heat Maps
At their core, heat maps utilize color gradients to represent data values. Areas with higher values are depicted in warmer colors (e.g., red, orange), while areas with lower values are represented in cooler colors (e.g., blue, green). This color scheme creates a visual hierarchy, highlighting areas of interest and enabling rapid identification of patterns and anomalies.
Applications of Heat Maps: A Multifaceted Tool
Heat maps find widespread application across diverse disciplines, offering valuable insights in various domains:
- Marketing and Sales: Analyzing website user behavior, identifying high-traffic areas, and understanding user interaction patterns.
- Business Intelligence: Identifying geographical trends, customer demographics, and market segmentation.
- Healthcare: Visualizing patient data, disease distribution, and treatment effectiveness.
- Finance: Analyzing stock market trends, portfolio performance, and risk assessment.
- Engineering: Identifying stress points in structures, optimizing product design, and analyzing material properties.
- Urban Planning: Visualizing population density, crime rates, and traffic flow patterns.
- Environmental Science: Mapping pollution levels, species distribution, and ecological changes.
Crafting Effective Heat Maps: A Step-by-Step Guide
1. Defining the Data and Objective:
- Data Selection: Choose relevant data that aligns with the desired analysis. This could include website clicks, customer demographics, sales figures, or environmental data.
- Objective Clarity: Define the specific question or hypothesis that the heat map aims to address. This provides a clear focus for data visualization and interpretation.
2. Choosing the Appropriate Visualization Tool:
-
Software Options: Numerous software tools are available for creating heat maps, each offering unique features and functionalities. Popular options include:
- Microsoft Excel: Offers basic heat map functionality through conditional formatting.
- Google Sheets: Provides similar capabilities to Excel with additional data visualization features.
- Tableau: A powerful data visualization platform with advanced heat map creation tools.
- Power BI: Another comprehensive business intelligence platform offering robust heat map creation capabilities.
- R and Python: Programming languages providing extensive libraries for data analysis and visualization, including heat map generation.
- Considerations: The choice of tool depends on the complexity of the data, desired visualization features, and user experience preferences.
3. Data Preparation and Transformation:
- Data Cleaning: Ensure data accuracy and consistency by removing outliers, handling missing values, and standardizing data formats.
- Data Transformation: Convert data into a suitable format for heat map visualization. This may involve aggregation, normalization, or scaling depending on the data type and analysis objective.
- Data Grouping: Group data into meaningful categories or regions for visual representation. This could involve clustering data points based on geographic location, time periods, or other relevant criteria.
4. Selecting the Appropriate Color Palette:
- Color Gradient: Choose a color gradient that effectively represents the data range. Consider using a continuous gradient for smoothly varying data or a discrete gradient for categorical data.
- Color Contrast: Ensure sufficient color contrast for clarity and readability. Avoid using colors that are visually similar or difficult to distinguish.
- Color Meaning: Assign colors with intuitive meaning. For example, warmer colors often represent higher values, while cooler colors represent lower values.
5. Designing the Heat Map Layout:
- Grid Structure: Define the grid structure of the heat map based on the data dimensions and visualization objectives.
- Axis Labels: Clearly label axes with appropriate units and descriptions to provide context and facilitate data interpretation.
- Legend: Include a legend to explain the color gradient and corresponding data values.
- **




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Creating Effective Heat Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!